Add extra readme files. |
||
|---|---|---|
| jobs | ||
| notebooks | ||
| scripts | ||
| .gitignore | ||
| BatchScoringJob.md | ||
| LICENSE | ||
| README.md | ||
| architecture.jpg | ||
README.md
Batch scoring of Spark machine learning models
Overview
This scenario demonstrates batch scoring of a Spark machine learning model on Azure Databricks. We use a predictive maintenance scenario where we classify machine sensor readings to classify a set of four machine components into healthy or unhealthy requiring maintenance states. The resulting supervised multi-class classifier model scores batches of new observations through a regularly scheduled Azure Databricks notebook jobs.
The solution uses methods from the PySpark MLlib machine learning library but the scoring process can be generalized to use any Python or R model hosted on Azure Databricks to make real-time predictions.
For an in depth description of the scenario, we have documented the operations in each of the supplied Jupyter notebooks contained in the ./notebooks/ directory of this repository.
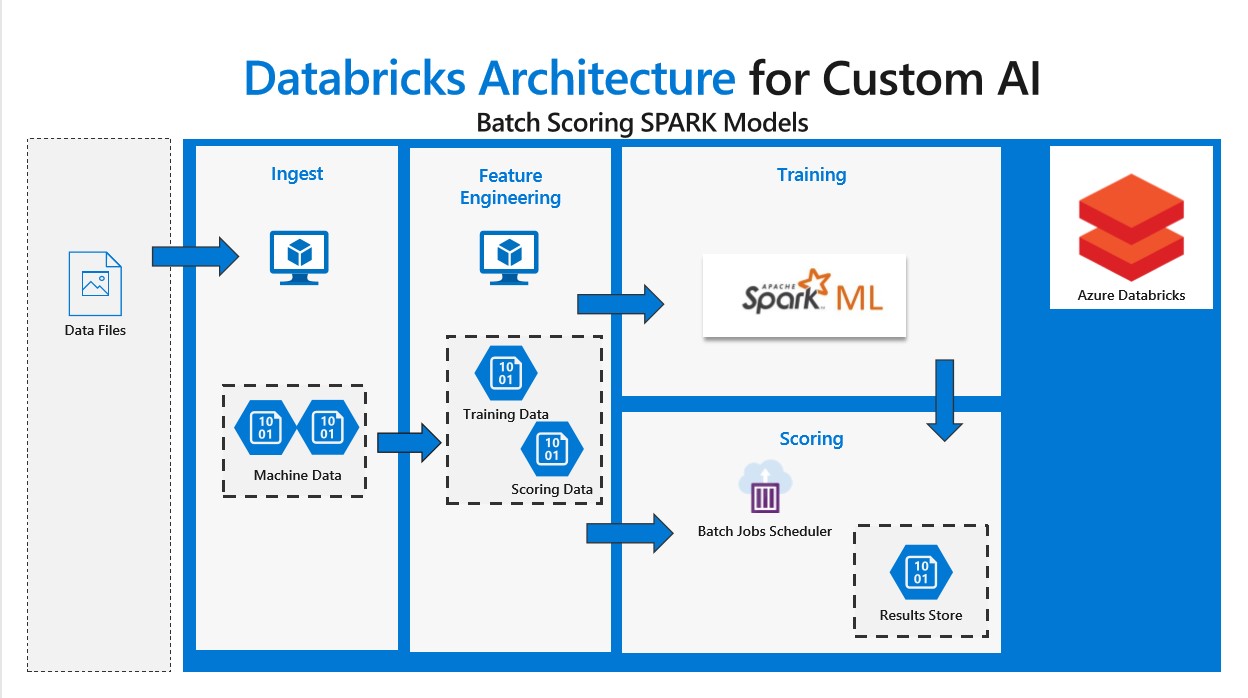
Design
This solution uses the Azure Databricks service. We create jobs that set up the batch scoring demonstration. Each job executes a Databricks notebook to prepare the data and create the full solution.
-
Ingest process downloads the simulated data sets from a GitHub site and converts and stores them as Spark dataframes on the Databricks DBFS. “Input Data” in the architecture diagram refers to a set of five simulated data sets related to realistic machine operating conditions.
-
Feature engineering transforms and combines the data sets into an analysis data set. The analysis data set can be targeted for training a model, or scoring data for a production pipeline. Each analysis data set is also stored in the Databricks DBFS.
-
Training process takes a subset of the complete data and constructs a model we can use to predict future outcomes. The model is stored in the Databricks DBFS for use by the scoring notebook.
-
The scoring process uses a different subset of the data, including data not yet collected to predict the current and future state of the machine. The model results are stored back onto the Databricks DBFS.
Prerequisites
-
We assume you have an Azure subscription. You will also need access to git on your working compute instance (local computer or VM). The repository is located at:
https://github.com/Azure/BatchSparkScoringPredictiveMaintenance -
Any working computer that has a web browser, and runs python Python Version > 2.7.9 or > 3.6 as specified for using the Databricks CLI.
Azure Databricks
This example is designed to run on Azure Databricks. Provision the service through your Azure supscription at the Azure portal.
- Search for
databricksand select the Azure Databricks. Follow the prompts, and selectStandard pricing tier. See https://azure.microsoft.com/en-us/pricing/details/databricks/ for information on different pricing tiers.
See https://docs.azuredatabricks.net/getting-started/index.html for detailed documentation on using Azure Databricks.
Databricks cluster
Once your Azure Databricks service has been created, you will need to create a compute cluster to execute the notebooks.
- From the portal, find your new Azure Databricks service, and
Launch Workspace. - A new window will open in your browser. Select the Clusters icon, and
Create Clusterto provision a new cluster with Python Version 3. The remaining defaults values are acceptable.
Databricks CLI
We will be using a Databricks command line utility (CLI) to automate running notebook tasks using the Databricks Jobs construct. Installing the Databricks CLI will simplify some of the operations required for this scenario. The first step is to import the Jupyter notebooks from the repository into your Databricks workspace. This can be accomplished with 1 command once the CLI is connected to your Azure Databricks instance.
From a command line, you can pip install the CLI using
pip install --upgrade databricks-cli
Setup
- Clone the GitHub repository:
git clone https://github.com/ehrlinger/BatchSparkScoringPredictiveMaintenance.git
- cd into the root directory of your cloned repository
The next two subsections of this document detail how to:
- Connect the CLI to your Databricks instance to simplify the import of repo notebooks.
- Import the repo notebooks into your Databricks workspace
Connect the CLI to your Databricks instance
We need to connect the CLI to your databricks instance. This can be done using a Databricks generated Authentication token. This linking only needs to be done once.
-
Copy the url portion of the web address of your Azure Databricks instance from your browser. You will not use the POST arguments for the hostname (everything including and following the '?' character). In
eastusregion, it will behttps://eastus.azuredatabricks.net/. -
Create and copy a an authentication token. Instructions are provided at the link above.
-
From your working machine command line,
databricks configure --token. This will prompt you for your Azure Databricks hostname and the authentication token.
Import Notebooks
Use the CLI to copy the scenario notebooks to your Databricks instance. From your working machine command line, change into the local copy of the repository. Then databricks workspace import_dir [OPTIONS] SOURCE_PATH TARGET_PATH
- The
SOURCE_PATHwill be the./notebooksdirectory. - The
TARGET_PATHwill include your user name, which you can get from the Azure Databricks UI, it should be related to your Azure AD email of the form<uname@example.com>. The whole[TARGET_PATH]should be of the form/Users/<uname@example.com>/notebooks.
The command should look like the following:
databricks workspace import_dir notebooks /Users/<uname@example.com>/notebooks
This will copy all required notebooks into the notebooks folder of your Azure Databricks Workspace.
To find these notebooks in your Azure Databricks Workspace, use the Workspace icon, follow the path to your /Users/<uname@example.com>/notebooks. Databricks uses Jupyter notebooks with some extensions. Instructions on how to use Jupyter notebooks are at https://docs.databricks.com/user-guide/notebooks/notebook-use.html#run-notebooks.
Steps
To create the full example scenario, through your Azure Databricks workspace, run through the following notebooks now located in your Azure Databricks workspacce.
These notebooks need to be run sequentially in alpha-numeric order, as each depends on data artifacts produced in the previous notebooks full run.
When running the notebooks, you may have to start your Azure Databricks cluster or attach these notebooks to your Azure Databricks cluster. The UI will prompt you if this is required.
- Ingest Data. Open the
1_data_ingestionnotebook on the Azure Databricks workspace. You can eitherRun Allcells, or execute cells individually. This notebook downloads the example data into your Azure Databricks Data storage. - Model Training Pipeline Open the
2_Training_Pipelinenotebook on the Azure Databricks workspace. You can eitherRun Allcells, or execute cells individually. This notebook will run two external notebooks.- Create a training data set with
2a_feature_engineering. The training data is written to the Azure Databricks Data store. Once this notebook is run, you can optionally examine the data created with the2a_feature_explorationnotebook. - Create a machine learning model with
2b_model_building. Once this notebook is run, you can optionally examine the model with the2b_model_testingnotebook with other data created with the2a_feature_engineeringnotebook. The model is stored on the Azure Databricks file system in parquet format.
- Create a training data set with
- Data Scoring Pipeline Open the
notebooks/3_Scoring_Pipelinenotebook on the Azure Databricks workspace. You can eitherRun Allcells, or execute cells individually. This notebook will also run two external notebooks.- Create a scoring data set with
2a_feature_engineeringwith different input parameters than in the training dataset. The scoring data is written to the Azure Databricks Data store. Once this notebook is run, you can again optionally examine the data created with the2a_feature_explorationnotebook. 3a_model_scoringwill score the data with the machine learning model created with2b_model_building. The results data is written to the Azure Databricks Data store. Once this notebook is run, you can optionally examine the scored results data with the3a_model_scoring_evaluationnotebook.
- Create a scoring data set with
- (optional) Instruction to create the batch scoring Databricks Job using the Databricks CLI are documented at https://github.com/Azure/BatchSparkScoringPredictiveMaintenance/blob/master/BatchScoringJob.md.
Conclusion
This scenario demonstrates how to automate the batch scoring of a predictive maintenance solution. The actual work of the "batch scoring a spark model" scenario is done through an Azure Databricks job. The job executes the 3_Scoring_Pipeline notebook, which depends on a machine learning model existing on the Azure Databricks file storage. We created the model using the 2_Training_Pipeline notebook which used the data downloaded with the 1_data_ingestion notebook.
Cleaning up
The easiest way to cleanup this work is to delete the resource group containing the Azure Databricks instance.
- Through the Azure portal (https://portal.azure.com) search for
databricks. - Open your Azure Databricks service and select the Resource Group link.
- Delete resource group will remove the Azure Databricks service and all associated resources including the notebooks and data artifacts used in this scenario.
You may also want to remove the Databricks CLI from your python environment with
pip uninstall databricks-cli
References
This scenario has been developed using a similar predictive maintenance use case published at following reference locations:
- Predictive Maintenance Solution Template
- Predictive Maintenance Modeling Guide
- Predictive Maintenance Modeling Guide using SQL R Services
- Predictive Maintenance Modeling Guide Python Notebook
- Predictive Maintenance using PySpark
- Predictive Maintenance scenario
- Deep learning for predictive maintenance
Contributing
This project welcomes contributions and suggestions. Most contributions require you to agree to a Contributor License Agreement (CLA) declaring that you have the right to, and actually do, grant us the rights to use your contribution. For details, visit https://cla.microsoft.com.
When you submit a pull request, a CLA-bot will automatically determine whether you need to provide a CLA and decorate the PR appropriately (e.g., label, comment). Simply follow the instructions provided by the bot. You will only need to do this once across all repos using our CLA.
This project has adopted the Microsoft Open Source Code of Conduct. For more information see the Code of Conduct FAQ or contact opencode@microsoft.com with any additional questions or comments.
Author:
John Ehrlinger john.ehrlinger@microsoft.com