As per discussion #105, commit
|
||
|---|---|---|
| .. | ||
| README.md | ||
| mirror-eventhub.config | ||
| mirror-maker-graphic.PNG | ||
| source-kafka.config | ||
README.md
Using Apache Kafka's MirrorMaker with Event Hubs for Apache Kafka Ecosystems
One major consideration for modern cloud scale apps is being able to update, improve, and change infrastructure without interrupting service. In this tutorial, we show how a Kafka-enabled Event Hub and Kafka MirrorMaker can integrate an existing Kafka pipeline into Azure by "mirroring" the Kafka input stream in the Event Hub service.
Prerequisites
To complete this tutorial, make sure you have:
- An Azure subscription. If you do not have one, create a free account before you begin.
- Java Development Kit (JDK) 1.7+
- On Ubuntu, run
apt-get install default-jdkto install the JDK. - Be sure to set the JAVA_HOME environment variable to point to the folder where the JDK is installed.
- On Ubuntu, run
- Download and install a Maven binary archive
- On Ubuntu, you can run
apt-get install mavento install Maven.
- On Ubuntu, you can run
- Git
- On Ubuntu, you can run
sudo apt-get install gitto install Git.
- On Ubuntu, you can run
Create an Event Hubs namespace
An Event Hubs namespace is required to send or receive from any Event Hubs service. See Create a Kafka-enabled Event Hub for instructions on getting an Event Hubs Kafka endpoint. Make sure to copy the Event Hubs connection string for later use.
FQDN
For these samples, you will need the connection string from the portal as well as the FQDN that points to your Event Hub namespace. The FQDN can be found within your connection string as follows:
Endpoint=sb://mynamespace.servicebus.windows.net/;SharedAccessKeyName=XXXXXX;SharedAccessKey=XXXXXX
If your Event Hubs namespace is deployed on a non-Public cloud, your domain name may differ (e.g. *.servicebus.chinacloudapi.cn, *.servicebus.usgovcloudapi.net, or *.servicebus.cloudapi.de).
Clone the example project
Now that you have a Kafka-enabled Event Hubs connection string, clone the Azure Event Hubs for Kafka repository and navigate to the tutorials/mirror-maker subfolder:
git clone https://github.com/Azure/azure-event-hubs-for-kafka.git
cd azure-event-hubs-for-kafka/tutorials/mirror-maker
Set up a Kafka cluster
Use the Kafka quickstart guide to set up a cluster with the desired settings (or use an existing Kafka cluster).
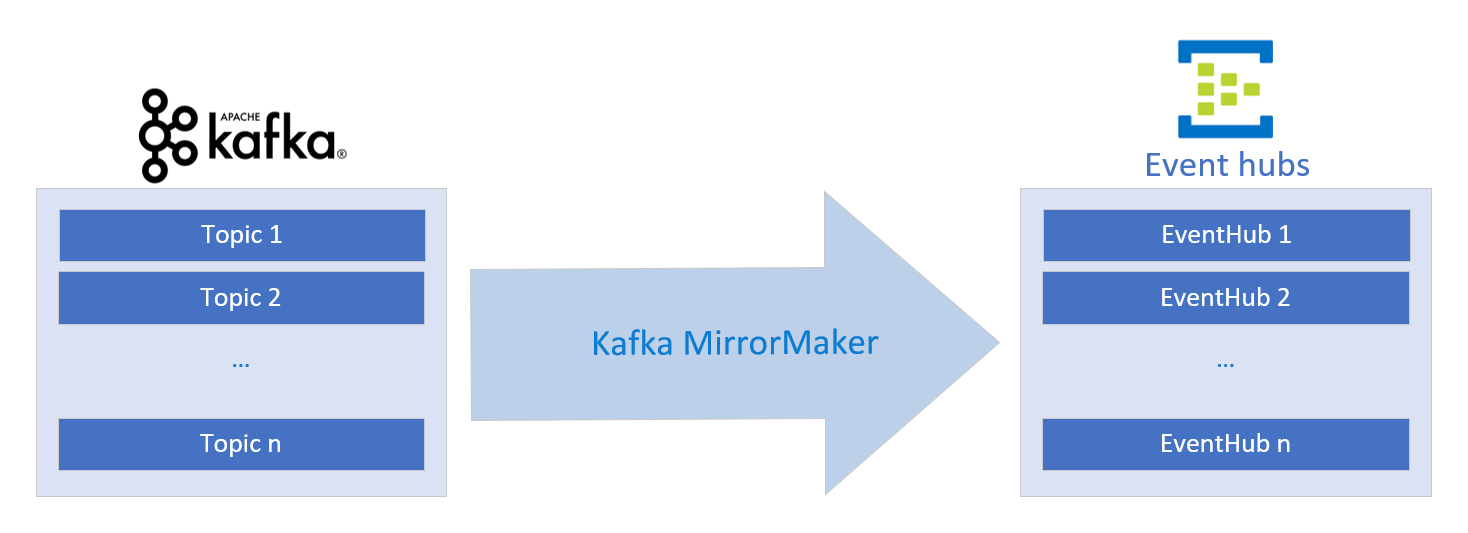
Kafka MirrorMaker
Kafka MirrorMaker allows for the "mirroring" of a stream. Given source and destination Kafka clusters, MirrorMaker will ensure any messages sent to the source cluster will be received by both the source and destination clusters. In this example, we'll show how to mirror a source Kafka cluster with a destination Kafka-enabled Event Hub. This scenario can be used to send data from an existing Kafka pipeline to Event Hubs without interrupting the flow of data.
Check out the Kafka Mirroring/MirrorMaker Guide for more detailed information on Kafka MirrorMaker.
Configuration
To configure Kafka MirrorMaker, we'll give it a Kafka cluster as its consumer/source and a Kafka-enabled Event Hub as its producer/destination.
Consumer Configuration
Update the consumer configuration file source-kafka.config, which tells MirrorMaker the properties of the source Kafka cluster.
source-kafka.config
bootstrap.servers={SOURCE.KAFKA.IP.ADDRESS1}:{SOURCE.KAFKA.PORT1},{SOURCE.KAFKA.IP.ADDRESS2}:{SOURCE.KAFKA.PORT2},etc
group.id=example-mirrormaker-group
exclude.internal.topics=true
client.id=mirror_maker_consumer
Producer Configuration
Now update the producer config file mirror-eventhub.config, which tells MirrorMaker to send the duplicated (or "mirrored") data to the Event Hubs service. Specifically change bootstrap.servers and sasl.jaas.config to point to your Event Hubs Kafka endpoint. The Event Hubs service requires secure (SASL) communication, which is achieved by setting the last three properties in the configuration below.
mirror-eventhub.config
bootstrap.servers=mynamespace.servicebus.windows.net:9093
client.id=mirror_maker_producer
#Required for Event Hubs
sasl.mechanism=PLAIN
security.protocol=SASL_SSL
sasl.jaas.config=org.apache.kafka.common.security.plain.PlainLoginModule required username="$ConnectionString" password="Endpoint=sb://mynamespace.servicebus.windows.net/;SharedAccessKeyName=XXXXXX;SharedAccessKey=XXXXXX";
Run MirrorMaker
Run the Kafka MirrorMaker script from the root Kafka directory using the newly updated configuration files. Make sure to update the path of the config files (or copy them to the root Kafka directory) in the following command.
bin/kafka-mirror-maker.sh --consumer.config source-kafka.config --num.streams 1 --producer.config mirror-eventhub.config --whitelist=".*"
To verify that events are making it to the Kafka-enabled Event Hub, check out the ingress statistics in the Azure portal, or run a consumer against the Event Hub.
Now that MirrorMaker is running, any events sent to the source Kafka cluster should be received by both the Kafka cluster and the mirrored Kafka-enabled Event Hub service. By using MirrorMaker and an Event Hubs Kafka endpoint, we can migrate an existing Kafka pipeline to the managed Azure Event Hubs service without changing the existing cluster or interrupting any ongoing data flow!