|
|
||
|---|---|---|
| .. | ||
| .images | ||
| Data-loading | ||
| Debugging/Compute | ||
| Environment | ||
| Operationalize | ||
| Training | ||
| README.md | ||
README.md
| page_type | languages | products | description | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| sample |
|
|
An official step-by-step guide of best-practices with techniques and optimizations for running large scale distributed training on AzureML. Includes all aspects of the data science steps to manage enterprise grade MLOps lifecycle from resource setup and data loading to training optimizations, evaluation and optimizations for inference. |
AzureML Large Scale Deep Learning Best Practices
Table of Contents
Welcome
This document is for engineers and researchers (both individuals and teams) interested in maximizing the performance of deep learning models in AzureML. We assume basic knowledge of machine learning and deep learning concepts.
Currently, there is an astonishing amount of toil and guesswork involved in actually getting deep neural networks to work well in practice. Our emphasis is to provide best practices for large scale training workloads to get highly efficient optimized performance using state of art technologies.
Optimizations for Deep Learning in AzureML
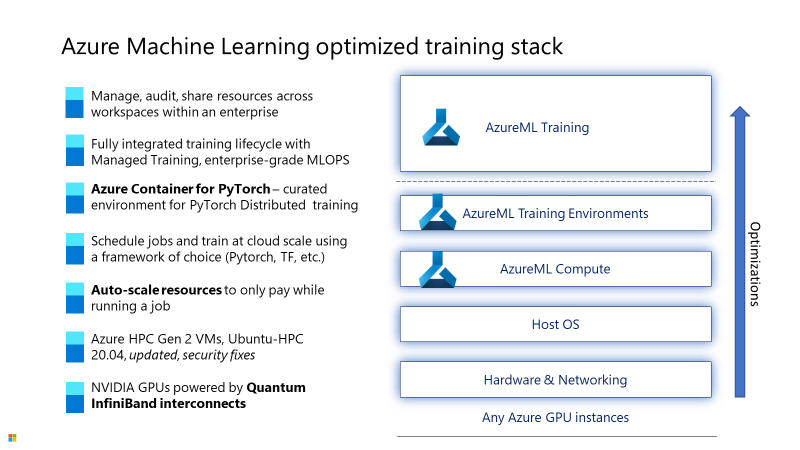
The execution of the training and inference deep learning graph uses capabilities from all the layers in the stack. There are inter-depedencies between the HW components and the SW drivers and libraries. The AzureML stack for deep learning provides a fully optimized environment that is validated and constantly updated to maximize the performance on the corresponding HW platform.
AzureML uses the high performance Azure AI hardware with networking infrastructure for high bandwidth inter-GPU communication. This is critical for the node level communication when executing D-H-P parallelism splitting the data, model or pipeline across many GPUs.
The host OS is updated with the latest drivers and patches to ensure smooth operation.
The AzureML Compute layer abstracts the complexities for managing the cloud scale infrastructure for compute, storage and networking.
AzureML supports curated environments for training execution on cached Docker images reducing the run preparation cost and consistency for experiment runs. The Azure Container for PyTorch (ACPT) Curated Environment is the built-in setup for running pytorch training experiments on the Azure AI hardware. ACPT includes a curated set of optimizer libraries to improve the training throughput with DeepSpeed for GPU memory optimization, ONNX Runtime Training for efficient op-level execution and NebulaML for fast checkpointing.
The AzureML PaaS offers capabilities for the enterprise MLOps lifecycle to manage all aspects of the experimentation and deployment loops.
This step-by-step guide is intended to help AzureML users setup, execute and manage their deep learning workloads with efficiency and agility.
Create ML resources to get started
Please follow this tutorial in order to create all the necessary resources to get started. You'll then have everything you need to get started with Azure Machine Learning. The AzureML Workspace is the top-level resource for your machine learning activities, providing a centralized place to view and manage the artifacts you create when you use Azure Machine Learning. The compute resources provide a pre-configured cloud-based environment you can use to train, deploy, automate, manage, and track machine learning models.
Register training dataset
After provisioning the workspace, the next step is to link it to the store where the training data resides. AzureML Datastores allow for the ability to securely connect to your storage services in Microsoft Azure without putting your authentication credentials or the integrity of your original data source at risk. They store connection information, like your subscription ID and token authorization in a secure Key Vault that's associated with the Azure Machine Learning workspace. In this way, you can securely access your storage without having to hard code connection information into your scripts. Please refer to these steps to create a datastore. Next, we'll need to define a data asset or a reference to the data source location along with associated metadata. AzureML supports thre data asset types:
- File: useful for read/write scenarios over a single file, of any format.
- Folder: useful for collection of parquet / CSV files to be loaded into Pandas / Spark or for Deep learning scenarios with images, text, audio, video files located in a folder.
- Table: for scenarios where you have a complex schema subject to frequent changes, or you need a subset of large tabular data. For more details on working with tables in AzureML please refer to this article.
Follow this guide to learn more how to create any of the supported data assets.
Create Training environment
An Environment is useful to track and reproduce the projects' software dependencies as they evolve over time. In this section you can learn more about Environments in AzureML, how to quickly get started and validate the setup before we begin training.
Efficient data loading for large training workloads
Because when training large AI models the costliest resource is the GPU on the compute clusters, we want to ensure hardware is fully utilized in order to keep costs as low as possible (no idle compute). Follow these best-practices on how to access data in a performant manner under different constraints and workloads when running high scale AI workloads.
Optimized Training for Large Models
In this section we're going to focus on optimizing the training phase of several of the most popular large deep learning model architectures. The goal is to get an efficient training loop, that can is highly scalable as we increase the training dataset size or add more compute nodes for getting results faster.