* added core docs * updated image * Updated ReadME * Removed Access Requirements ReadMEFile * Update DataManagement reference * Updated doc * fixed a few typos + visual changes Co-authored-by: Marvin Buss <marvin.buss@gmail.com> |
||
|---|---|---|
| .ado/workflows | ||
| .github | ||
| code | ||
| configs | ||
| docs | ||
| infra | ||
| .gitattributes | ||
| .gitignore | ||
| CODE_OF_CONDUCT.md | ||
| LICENSE | ||
| README.md | ||
| SECURITY.md | ||
README.md
Enterprise Scale Analytics - Data Management
General disclaimer Please be aware that this template is in public preview. Therefore, expect smaller bugs and issues when working with the solution. Please submit an Issue, if you come across any issues that you would like us to fix.
Description
The Data Management template is, as the name suggessts, classified as a management function and is at the heart of the Enterprise Scale Analytics platform. It is responsible for the governance of the platform and enables communication to ingest data sources from Azure, 3rd Party Clouds and On-Premises data sources.
What will be deployed?
By default, all the services which comes under Data Management Zone are enabled and you must explicitly disable them if you don't want it to be deployed.

- Virtual Network
- Network Security Groups
- Route Tables
- Azure Firewall
- Firewall Policy
- Private DNS Zones
- Container Registry
- Purview
- Key Vault
- Storage Account
- Synapse PL Hub
- PowerBI
- Policies
For more details regarding the services which will be deployed, please check Data Management.
You have two options for deploying this reference architecture:
- Use the
Deploy to AzureButton or - Use GitHub Actions or Azure DevOps Pipelines
Prerequisites
The following prerequisites are required to make this repository work:
- An Azure subscription
- User Access Administrator or Owner access to the subscription to be able to create a service principal and role assignments for it.
If you don’t have an Azure subscription, create your Azure free account today.
Option 1: Deploy to Azure - Quickstart
| Data Management Zone |
|---|
| |
Option 2: GitHub Actions or Azure DevOps Pipelines
1. Create repository from a template
- On GitHub, navigate to the main page of the repository.
- Above the file list, click Use this template

- Use the Owner drop-down menu, and select the account you want to own the repository.

- Type a name for your repository, and an optional description.
- Choose a repository visibility. For more information, see "About repository visibility."
- Optionally, to include the directory structure and files from all branches in the template, and not just the default branch, select Include all branches.
- Click Create repository from template.
2. Setting up the required Service Principal and access
A service principal needs to be generated for authentication and authorization from GitHub or Azure DevOps to your Azure subscription. This is required to deploy resources to your environment. Just go to the Azure Portal to find the id of your subscription. Then start CLI or PowerShell, login to Azure, set the Azure context and execute the following commands to generate the required credentials:
Azure CLI
# Replace {service-principal-name} and {subscription-id} with your
# Azure subscription id and any name for your service principal.
az ad sp create-for-rbac \
--name "{service-principal-name}" \
--role "Contributor" \
--scopes "/subscriptions/{subscription-id}" \
--sdk-auth
Azure Powershell
# Replace {service-principal-name} and {subscription-id} with your
# Azure subscription id and any name for your service principal.
New-AzADServicePrincipal `
-DisplayName "{service-principal-name}" `
-Role "Contributor" `
-Scope "/subscriptions/{subscription-id}"
This will generate the following JSON output:
{
"clientId": "<GUID>",
"clientSecret": "<GUID>",
"subscriptionId": "<GUID>",
"tenantId": "<GUID>",
(...)
}
Take note of the output. It will be required for the next steps.
Now you can choose, whether you would like to use GitHub Actions or Azure DevOps for your deployment.
3. a) GitHub Actions
If you want to use GitHub Actions for deploying the resources, add the previous JSON output as a repository secret with the name AZURE_CREDENTIALS in your GitHub repository:

To do so, execute the following steps:
- On GitHub, navigate to the main page of the repository.
- Under your repository name, click on the Settings tab.
- In the left sidebar, click Secrets.
- Click New repository secret.
- Type the name
AZURE_CREDENTIALSfor your secret in the Name input box. - Enter the JSON output from above as value for your secret.
- Click Add secret.
3. b) Azure DevOps
If you want to use Azure DevOps Pipelines for deploying the resources, you need to create an Azure Resource Manager service connection. To do so, execute the following steps:
- First, you need to create an Azure DevOps Project. Instructions can be found here.
- In Azure DevOps, open the Project settings.
- Now, select the Service connections page from the project settings page.
- Choose New service connection and select Azure Resource Manager.

- On the next page select Service principal (manual).
- Select the appropriate environment to which you would like to deploy the templates. Default and tested option is Azure Cloud.
- For the Scope Level, select Subscription and enter your
subscription Idandname. - Enter the details of the service principal that we have generated in step 3. (Service Principal Id = clientId, Service Principal Key = clientSecret, Tenant ID = tenantId) and click on Verify to make sure that the connection works.
- Enter a user-friendly Connection name to use when referring to this service connection. Take note of the name, because this will be required in the parameter update process.
- Optionally, enter a Description.
- Click on Verify and save.

More information can be found here.
4. Parameter Update Process
In order to deploy the ARM templates in this repository to the desired Azure subscription, you'll need to modify some parameters in the forked repository. As updating each parameter file manually is a time consuming process, which could lead as well to undesired user errors, we have simplified the process with a GitHub Action workflow. After successfully executing the previous steps, please open the /.github/workflows/updateParameters.yml" YAML file. In this file you need to update the environment variables. Once you commit the file with the updated values, a GitHub Action workflow will be triggered that replaces all parameters accordingly. Just click on /.github/workflows/updateParameters.yml" and edit the following section:
env:
DATA_HUB_SUBSCRIPTION_ID: '{dataHubSubscriptionId}'
DATA_HUB_NAME: '{dataHubName}' # Choose max. 11 characters. They will be used as a prefix for all services. If not unique, deployment can fail for some services.
LOCATION: '{regionName}' # Specifies the region for all services (e.g. 'northeurope', 'eastus', etc.)
AZURE_RESOURCE_MANAGER_CONNECTION_NAME: '{resourceManagerConnectionName}'
The parameters have the following meaning:
| Parameter | Description | Sample value |
|---|---|---|
| DATA_HUB_SUBSCRIPTION_ID | Specifies the subscription ID of the Data Management Zone where all the resources will be deployed | xxxxxxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxxxxxx |
| DATA_HUB_NAME | Specifies the name of your Data Management Zone. The value should consist of alphanumeric characters (A-Z, a-z, 0-9) and should not contain any special characters like -, _, ., etc. Special characters will be removed in the renaming process. |
myhub01 |
| LOCATION | Specifies the region where you want the resources to be deployed. | northeurope |
| AZURE_RESOURCE_MANAGER _CONNECTION_NAME | Specifies the resource manager connection name in Azure DevOps. You can leave the default value, if you want to use GitHub Actions for your deployment. More details on how to create the resource manager connection in Azure DevOps can be found in step 4. b) or here. | my-connection-name |
After updating the values, please commit the updated version to the main branch. This will kick off a GitHub Action workflow, which will appear under the Actions tab of the main page of the repository. The Update Parameter Files workflow will update all parameters in your repository according to a pre-defined naming convention. Once the process has finished, it will open a Pull Request in your repository, where you can review the changes made by the workflow. Please follow the instructions in the Pull Request to complete the parameter update process. We are not renaming the environment variables in the workflow files, because this can have the undesired outcome of triggering an infinite number of workflows.
After following the instructions in the Pull request, you can merge the pull request back into the main branch of your repository by clicking on Merge pull request. Finally, you can click on Delete branch to clean up your repository.
5. (not applicable for GH Actions) Reference pipeline from GitHub repository in Azure DevOps pipelines
1. Install Azure DevOps Pipelines GitHub Application
First you need to add and install the Azure Pipelines GitHub App to your GitHub account. To do so, execute the following steps:
- Click on Marketplace in the top navigation bar on GitHub.
- In the Marketplace, search for Azure Pipelines. The Azure Pipelines offering is free for anyone to use for public repositories, and free for a single build queue if you’re using a private repository.

- Select it and click on Install it for free.

- If you are part of multiple GitHub organisations, select the one you forked this repository to from the Switch billing account dropdown menu.
- You may be prompted to confirm your GitHub password to continue.
- You may be prompted to log in to your Microsoft account. Make sure you are logged into the one taht is associated with your Azure DevOps account.
2. Configuring Azure Pipelines project
As a last step, you need to reference the Azure DevOps Yaml pipeline, that is stored in your GitHub repository, as a Pipeline in your Azure DevOps Project. To do so, execute the following steps:
- Select the project, where you have setup your
Resource Manager Connection. - Select Pipelines and then New Pipeline in order to create a new pipeline.
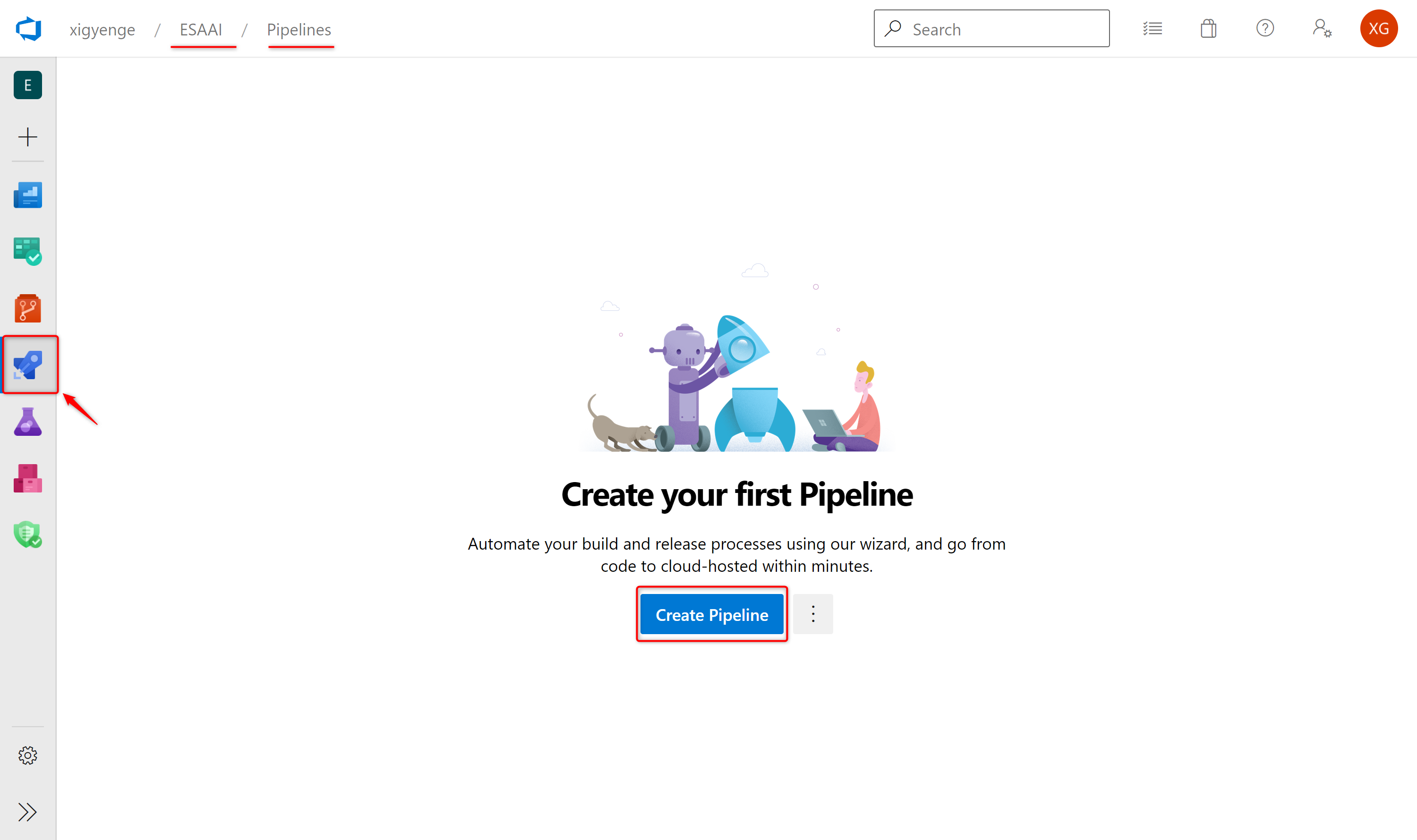
- Choose GitHub
YAMLand search for your repository (e.g. "GitHubUserName/RepositoryName").

- Select your respository.
- Click on Existing Azure Pipelines in YAML file
- Select
mainas branch and/.ado/workflows/dataNodeDeployment.ymlas path.
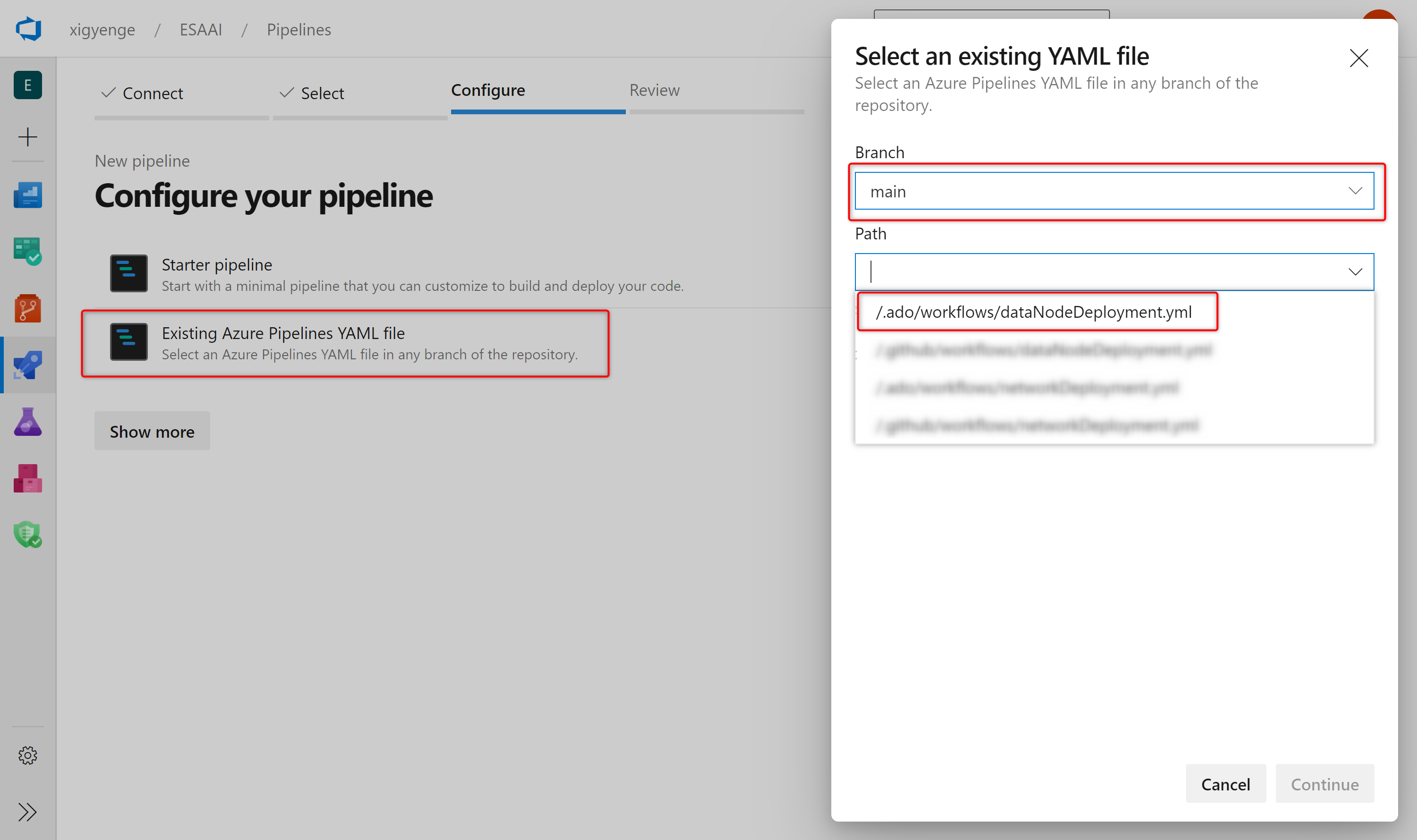
- Click on Continue and then on Run.
6. Follow the workflow deployment
Congratulations! You have successfully executed all steps to deploy the template into your environment through GitHub Actions or Azure DevOps.
If you are using GitHub Actions, you can navigate to the Actions tab of the main page of the repository, where you will see a workflow with the name Data Management Deployment running. Click on it to see how it deploys one service after another. If you run into any issues, please open an issue here.
If you are using Azure DevOps Pipelines, you can navigate to the pipeline that you have created as part of step 6 and follow how it deploys one service after another. If you run into any issues, please open an issue here.
Enterprise Scale Analytics Documentation and Implementation
- Documentation
- Implementation - Data Management
- Implementation - Data Landing Zone
- Implementation - Data Domain - Batch
- Implementation - Data Domain - Streaming
- Implementation - Data Product - Reporting
- Implementation - Data Product - Analytics & Data Science
Contributing
This project welcomes contributions and suggestions. Most contributions require you to agree to a Contributor License Agreement (CLA) declaring that you have the right to, and actually do, grant us the rights to use your contribution. For details, visit https://cla.opensource.microsoft.com.
When you submit a pull request, a CLA bot will automatically determine whether you need to provide a CLA and decorate the PR appropriately (e.g., status check, comment). Simply follow the instructions provided by the bot. You will only need to do this once across all repos using our CLA.
This project has adopted the Microsoft Open Source Code of Conduct. For more information see the Code of Conduct FAQ or contact opencode@microsoft.com with any additional questions or comments.