* put images into vignette folder * Created 00-azure-introduction.md * Created 10-vm-sizes.md * Update VM sizes link in docs/README.md * Create 20-package-management.md * Updated README.md with Azure Batch limitations * Create 21-distributing-data.md * Create 22-parallelizing-cores.md * Create 23-persistent-storage.md * standardized foreach keyword and pool keyword |
||
|---|---|---|
| R | ||
| docs | ||
| vignettes | ||
| .Rbuildignore | ||
| .gitignore | ||
| DESCRIPTION | ||
| LICENSE | ||
| NAMESPACE | ||
| README.md | ||
README.md
doAzureParallel
The doAzureParallel package is a parallel backend for the widely popular foreach package. With doAzureParallel, each iteration of the foreach loop runs in parallel on an Azure Virtual Machine (VM), allowing users to scale up their R jobs to tens or hundreds of machines.
doAzureParallel is built to support the foreach parallel computing package. The foreach package supports parallel execution - it can execute multiple processes across some parallel backend. With just a few lines of code, the doAzureParallel package helps create a pool in Azure, register it as a parallel backend, and seamlessly connects to the foreach package.
Dependencies
- R (>= 3.3.1)
- httr (>= 1.2.1)
- rjson (>= 0.2.15)
- RCurl (>= 1.95-4.8)
- digest (>= 0.6.9)
- foreach (>= 1.4.3)
- iterators (>= 1.0.8)
Installation
Install doAzureParallel directly from Github.
# install the package devtools
install.packages("devtools")
library(devtools)
# install the doAzureParallel and rAzureBatch package
install_github(c("Azure/rAzureBatch", "Azure/doAzureParallel"))
Azure Requirements
To run your R code across a pool in Azure, we'll need to get keys and account information.
Setup Azure Account
First, set up your Azure Account (Get started for free!)
Once you have an Azure account, you'll need to create the following two services in the Azure portal:
- Azure Batch Account (Create an Azure Batch Account in the Portal)
- Azure Storage Account (this can be created with the Batch Account)
Get Keys and Account Information
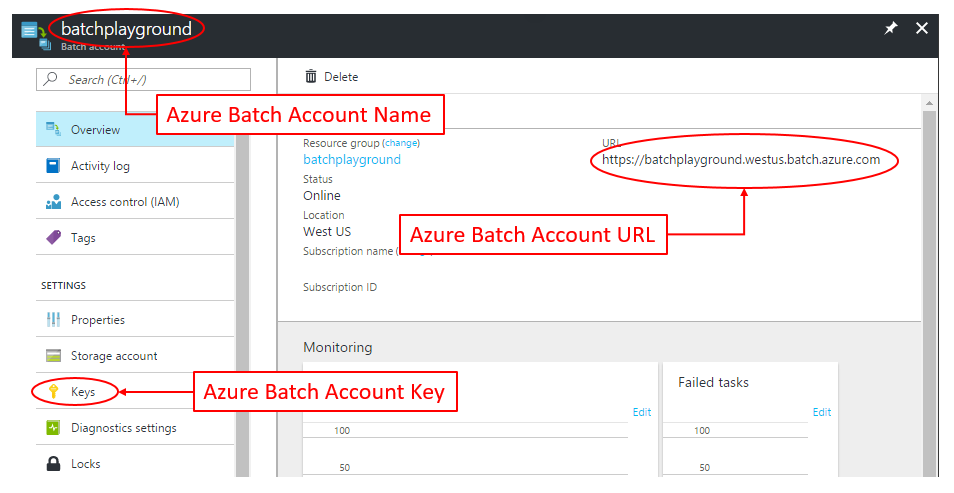
For your Azure Batch Account, we need to get:
- Batch Account Name
- Batch Account URL
- Batch Account Access Key
This information can be found in the Azure Portal inside your Batch Account:
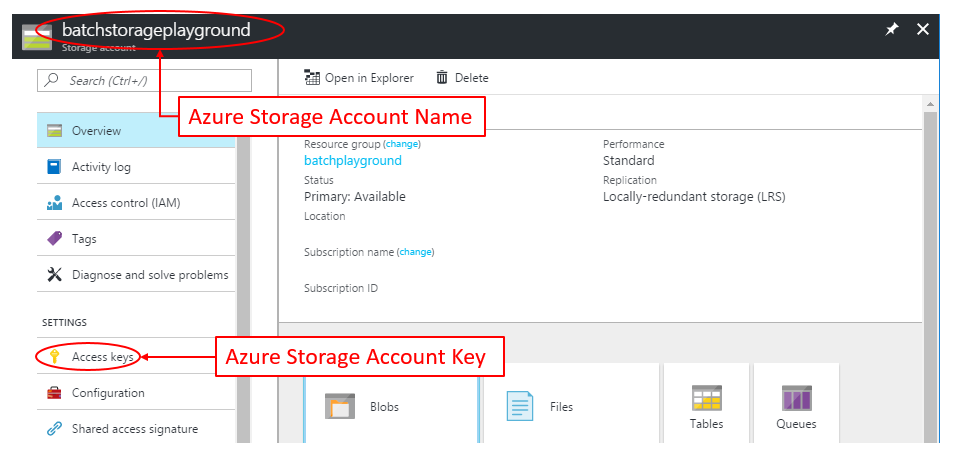
For your Azure Storage Account, we need to get:
- Storage Account Name
- Storage Account Access Key
This information can be found in the Azure Portal inside your Azure Storage Account:
Keep track of the above keys and account information as it will be used to connect your R session with Azure.
Getting Started
Import the package
library(doAzureParallel)
Set up your parallel backend with Azure
# 1. Generate a pool configuration file.
generatePoolConfig("my_pool_config.json")
# 2. Edit your pool configuration file.
# Enter your Azure Batch Account & Azure Storage keys/account-info and configure your pool settings.
# 3. Register the pool. This will create a new pool if your pool hasn't already been provisioned.
pool <- registerPool("my_pool_config.json")
# 4. Register the pool as your parallel backend
registerDoAzureParallel
# 5. Check that your parallel backend has been registered
getDoParWorkers()
Run your parallel foreach loop with the %dopar% keyword. The foreach function will return the results of your parallel code.
number_of_iterations <- 10
results <- foreach(i = 1:number_of_iterations) %dopar% {
# This code is executed, in parallel, across your Azure pool.
}
When developing at scale, it is always recommended that you test and debug your code locally first. Switch between %dopar% and %do% to toggle between running in parallel on Azure and running in sequence on your local machine.
# run your code sequentially on your local machine
results <- foreach(i = 1:number_of_iterations) %do% { ... }
# use the doAzureParallel backend to run your code in parallel across your Azure pool
results <- foreach(i = 1:number_of_iterations) %dopar% { ... }
Pool Configuration JSON
Use your pool configuration JSON file to define your pool in Azure.
{
"batchAccount": {
"name": <Azure Batch Account Name>,
"key": <Azure Batch Account Key>,
"url": <Azure Batch Account URL>,
"pool": {
"name": <your pool name>, // example: "my_new_azure_pool"
"vmsize": <your pool VM size name>, // example: "Standard_A1_v2"
"poolSize": {
"targetDedicated": <number of node you want in your pool>, // example: 10
}
},
"rPackages": {
"cran": {
"source": "http://cran.us.r-project.org",
"name": ["some_cran_package", "some_other_cran_package"]
},
"github": ["username/some_github_package", "another_username/some_other_github_package"]
}
},
"storageAccount": {
"name": <Azure Storage Account Name>,
"key": <Azure Storage Account Key>
},
"settings": {
"verbose": false
}
}
Azure Pool Limitations
doAzureParallel is built on top of Azure Batch, which starts with a few quota limitations.
Core Count Limitation
By default, doAzureParallel users are limited to 20 cores in total. (Please refer to the VM Size Table to see how many cores are in the VM size you have selected.)
Our default VM size selection is the "Standard_A1_v2" that has 1 core per VM. With this VM size, users are limited to a 20-node pool.
Number of foreach Loops
By default, doAzureParallel users are limited to running 20 foreach loops that run on Azure in succession. This is because each foreach loops generates a job, of which users are by default limited to 20. To go beyond that, users need to delete their jobs.
Increasing Your Quota
To increase your default quota limitations, please visit this page for instructions.
Contributing
This project has adopted the Microsoft Open Source Code of Conduct. For more information see the Code of Conduct FAQ or contact opencode@microsoft.com with any additional questions or comments.