|
|
||
|---|---|---|
| .. | ||
| HDI-Spark/Notebooks | ||
| README.md | ||
| db-init.sh | ||
| install-worker.sh | ||
README.md
Deploying your App on the Cloud
Table of Contents
- Pre-requisites
- Preparing Worker Dependencies
- Preparing your Spark .NET App
- Cloud Deployment
Pre-requisites:
-
Tool to copy files to a distributed file system.
- ADLS, WASB → Azure Storage Explorer
- S3 → AWS CLI
- DBFS → Databricks CLI
-
Download install-worker.sh to your local machine. This is a helper script that we will use later in the installation section to copy Spark .NET dependent files into your Spark cluster's worker nodes. install-worker.sh takes in three parameters:
- The Cloud Provider:
azureoraws - URI where
Microsoft.Spark.Worker.<release>.tar.gzis uploaded (see the Microsoft.Spark.Worker section for instructions on where to download this) - Path on the executor node where the worker package will be installed (the path should be the directory that
yarnuser has access to).
Example Usage:
install-worker.sh azure adl://<cluster name>.azuredatalakestore.net/<some dir>/Microsoft.Spark.Worker.<release>.tar.gz /usr/local/bin - The Cloud Provider:
Preparing Worker Dependencies
Microsoft.Spark.Worker is a backend component that lives on the individual worker nodes of your Spark cluster. When you want to execute a C# UDF (user-defined function), Spark needs to understand how to launch the .NET CLR to execute this UDF. Microsoft.Spark.Worker provides a collection of classes to Spark that enable this functionality.
Microsoft.Spark.Worker
- Select a Microsoft.Spark.Worker Linux netcoreapp release to be deployed on your cluster.
- For example, if you want
.NET for Apache Spark v0.1.0usingnetcoreapp2.1, you'd download Microsoft.Spark.Worker.netcoreapp2.1.linux-x64-0.1.0.tar.gz.
- For example, if you want
- Upload
Microsoft.Spark.Worker.<release>.tar.gzand install-worker.sh to a distributed file system (e.g., HDFS, WASB, ADLS, S3, DBFS) that your cluster has access to.
Preparing your Spark .NET App
- Follow the Get Started guide to build your app.
- Publish your Spark .NET
appas self-contained.# For example, you can run the following on Linux. foo@bar:~/path/to/app$ dotnet publish -c Release -f netcoreapp2.1 -r ubuntu.16.04-x64 - Produce
<your app>.zipfor the published files.# For example, you can run the following on Linux using `zip`. foo@bar:~/path/to/app/bin/Release/netcoreapp2.1/ubuntu.16.04-x64/publish$ zip -r <your app>.zip . - Upload the following to a distributed file system (e.g., HDFS, WASB, ADLS, S3, DBFS) that your cluster has access to:
microsoft-spark-<version>.jar(Included as part of the Microsoft.Spark nuget and is colocated in your app's build output directory)<your app>.zip- Files (e.g., dependency files, common data accessible to every worker) or Assemblies (e.g., DLLs that contain your user-defined functions, libraries that your
appdepends on) to be placed in the working directory of each executor.
Cloud Deployment
Azure HDInsight Spark
Azure HDInsight Spark is the Microsoft implementation of Apache Spark in the cloud that allows users to launch and configure Spark clusters in Azure. You can use HDInsight Spark clusters to process your data stored in Azure (e.g., Azure Storage and Azure Data Lake Storage).
Note: Azure HDInsight Spark is Linux-based. Therefore, if you are interested in deploying your app to Azure HDInsight Spark, make sure your app is .NET Standard compatible and that you use .NET 6 compiler to compile your app.
Deploy Microsoft.Spark.Worker
Note that this step is required only once
Run HDInsight Script Action
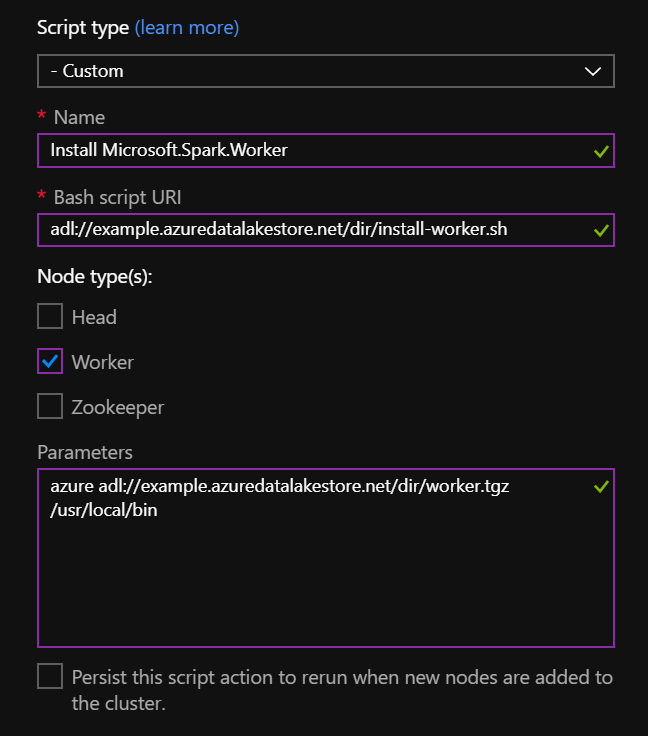
Run install-worker.sh on the cluster using HDInsight Script Actions:
- Script type: Custom
- Name: Install Microsoft.Spark.Worker (or anything that is descriptive)
- Bash script URI: The URI to which you uploaded
install-worker.sh(e.g. adl://<cluster name>.azuredatalakestore.net/<some dir>/install-worker.sh) - Node type(s): Worker
- Parameters: Parameters to
install-worker.sh. For example, if you uploaded to Azure Data Lake then it would beazure adl://<cluster name>.azuredatalakestore.net/<some dir>/Microsoft.Spark.Worker.<release>.tar.gz /usr/local/bin.
The following captures the setting for a HDInsight Script Action:
Run your app on the cloud!
Using spark-submit
sshinto one of the head nodes in the cluster.- Run
spark-submit:foo@bar:~$ $SPARK_HOME/bin/spark-submit \ --master yarn \ --class org.apache.spark.deploy.dotnet.DotnetRunner \ --files <comma-separated list of assemblies that contain UDF definitions, if any> \ adl://<cluster name>.azuredatalakestore.net/<some dir>/microsoft-spark-<version>.jar \ adl://<cluster name>.azuredatalakestore.net/<some dir>/<your app>.zip <your app> <app arg 1> <app arg 2> ... <app arg n>
Using Apache Livy
You can use Apache Livy, the Apache Spark REST API, to submit Spark .NET jobs to an Azure HDInsight Spark cluster as documented in Remote jobs with Apache Livy.
# For example, you can run the following on Linux using `curl`.
foo@bar:~$ curl -k -v -X POST "https://<your spark cluster>.azurehdinsight.net/livy/batches" \
-u "<hdinsight username>:<hdinsight password>" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-H "X-Requested-By: <hdinsight username>" \
-d @- << EOF
{
"file":"adl://<cluster name>.azuredatalakestore.net/<some dir>/microsoft-spark-<version>.jar",
"className":"org.apache.spark.deploy.dotnet.DotnetRunner",
"files":["adl://<cluster name>.azuredatalakestore.net/<some dir>/<udf assembly>", "adl://<cluster name>.azuredatalakestore.net/<some dir>/<file>"],
"args":["adl://<cluster name>.azuredatalakestore.net/<some dir>/<your app>.zip","<your app>","<app arg 1>","<app arg 2>,"...","<app arg n>"]
}
EOF
Amazon EMR Spark
Amazon EMR is a managed cluster platform that simplifies running big data frameworks on AWS.
Note: AWS EMR Spark is Linux-based. Therefore, if you are interested in deploying your app to AWS EMR Spark, make sure your app is .NET Standard compatible and that you use .NET 6 compiler to compile your app.
Deploy Microsoft.Spark.Worker
Note that this step is only required at cluster creation
Create cluster using Amazon EMR Bootstrap Actions
Run install-worker.sh during cluster creation using Bootstrap Actions.
# For example, you can run the following on Linux using `aws` cli.
foo@bar:~$ aws emr create-cluster \
--name "Test cluster" \
--release-label emr-5.23.0 \
--use-default-roles \
--ec2-attributes KeyName=myKey \
--applications Name=Spark \
--instance-count 3 \
--instance-type m1.medium \
--bootstrap-actions Path=s3://mybucket/<some dir>/install-worker.sh,Name="Install Microsoft.Spark.Worker",Args=["aws","s3://mybucket/<some dir>/Microsoft.Spark.Worker.<release>.tar.gz","/usr/local/bin"]
Run your app on the cloud!
Using spark-submit
sshinto one of the nodes in the cluster.- Run
spark-submit:foo@bar:~$ spark-submit \ --master yarn \ --class org.apache.spark.deploy.dotnet.DotnetRunner \ --files <comma-separated list of assemblies that contain UDF definitions, if any> \ s3://mybucket/<some dir>/microsoft-spark-<version>.jar \ s3://mybucket/<some dir>/<your app>.zip <your app> <app args>
Using Amazon EMR Steps
Amazon EMR Steps can be used to submit jobs to the Spark framework installed on the EMR cluster.
# For example, you can run the following on Linux using `aws` cli.
foo@bar:~$ aws emr add-steps \
--cluster-id j-xxxxxxxxxxxxx \
--steps Type=spark,Name="Spark Program",Args=[--master,yarn,--files,s3://mybucket/<some dir>/<udf assembly>,--class,org.apache.spark.deploy.dotnet.DotnetRunner,s3://mybucket/<some dir>/microsoft-spark-<version>.jar,s3://mybucket/<some dir>/<your app>.zip,<your app>,<app arg 1>,<app arg 2>,...,<app arg n>],ActionOnFailure=CONTINUE
Databricks
Databricks is a platform that provides cloud-based big data processing using Apache Spark.
Note: Azure and AWS Databricks is Linux-based. Therefore, if you are interested in deploying your app to Databricks, make sure your app is .NET Standard compatible and that you use .NET 6 compiler to compile your app.
Databricks allows you to submit Spark .NET apps to an existing active cluster or create a new cluster everytime you launch a job. This requires the Microsoft.Spark.Worker to be installed first before you submit a Spark .NET app.
Deploy Microsoft.Spark.Worker
Note that this step is required only once
-
Download db-init.sh and install-worker.sh onto your local machine
-
Modify db-init.sh appropriately to point to the Microsoft.Spark.Worker release you want to download and install on your cluster
-
Download and install Databricks CLI
-
Setup authentication details for the Databricks CLI appropriately
-
Upload the files you downloaded and modified to your Databricks cluster
cd <path-to-db-init-and-install-worker> databricks fs cp db-init.sh dbfs:/spark-dotnet/db-init.sh databricks fs cp install-worker.sh dbfs:/spark-dotnet/install-worker.sh -
Go to your Databricks cluster homepage -> Clusters (on the left-side menu) -> Create Cluster
-
After configuring the cluster appropriately, set the init script (see the image below) and create the cluster.
Note: If everything went well, your cluster creation should have been successful. You can check this by clicking on the cluster -> Event Logs.
Run your app on the cloud!
Using Set JAR
Note: This approach allows job submission to an existing active cluster.
One-time Setup:
-
Go to your Databricks cluster -> Jobs (on the left-side menu) -> Set JAR
-
Upload the appropriate
microsoft-spark-<version>.jar -
Set the params appropriately:
Main Class: org.apache.spark.deploy.dotnet.DotnetRunner Arguments /dbfs/apps/<your-app-name>.zip <your-app-name>Note:
<your-app-name>is a name for the executable that you published. -
Configure the Cluster to point to an existing cluster (that you already set the init script for - see previous section).
Publishing your App & Running:
- You should first publish your app.
Note: Do not use
SparkSession.Stop()in your application code when submitting jobs to an existing active cluster. - Use Databricks CLI to upload your application to Databricks cluster. For instance,
cd <path-to-your-app-publish-directory> databricks fs cp <your-app-name>.zip dbfs:/apps/<your-app-name>.zip - This step is only required if app assemblies (e.g., DLLs that contain user-defined functions along with their dependencies) need to be placed in the working directory of each Microsoft.Spark.Worker.
- Upload your application assemblies to your Databricks cluster
cd <path-to-your-app-publish-directory> databricks fs cp <assembly>.dll dbfs:/apps/dependencies - Uncomment and modify the app dependencies section in db-init.sh to point to your app dependencies path and upload to your Databricks cluster.
cd <path-to-db-init-and-install-worker> databricks fs cp db-init.sh dbfs:/spark-dotnet/db-init.sh - Restart your cluster.
- Upload your application assemblies to your Databricks cluster
- Now, go to your
Databricks cluster -> Jobs -> [Job-name] -> Run Nowto run your job!
Using spark-submit
Note: This approach allows submission ONLY to cluster that gets created on-demand.
- Create a Job and select Configure spark-submit.
- Configure
spark-submitwith the following parameters:["--files","/dbfs/<path-to>/<app assembly/file to deploy to worker>","--class","org.apache.spark.deploy.dotnet.DotnetRunner","/dbfs/<path-to>/microsoft-spark-<version>.jar","/dbfs/<path-to>/<app name>.zip","<app name>","app arg1","app arg2"]