Fixes #124 Signed-off-by: Dave Thaler <dthaler@ntdev.microsoft.com> |
||
|---|---|---|
| .github | ||
| docs | ||
| ebpfapi | ||
| ebpfcore | ||
| external | ||
| include | ||
| libs | ||
| netebpfext | ||
| scripts | ||
| tests | ||
| tools | ||
| .clang-format | ||
| .gitattributes | ||
| .gitignore | ||
| .gitmodules | ||
| CONTRIBUTING.md | ||
| LICENSE.txt | ||
| README.md | ||
| ebpf-for-windows.sln | ||
README.md
eBPF on Windows
eBPF is a well-known technology for providing programmability and agility, especially for extending an OS kernel, for use cases such as DoS protection and observability. This project is a work-in-progress that allows using existing eBPF toolchains and APIs familiar in the Linux ecosystem to be used on top of Windows. That is, this project takes existing eBPF projects as submodules and adds the layer in between to make them run on top of Windows.
New to eBPF?
See our eBPF tutorial.
Architectural Overview
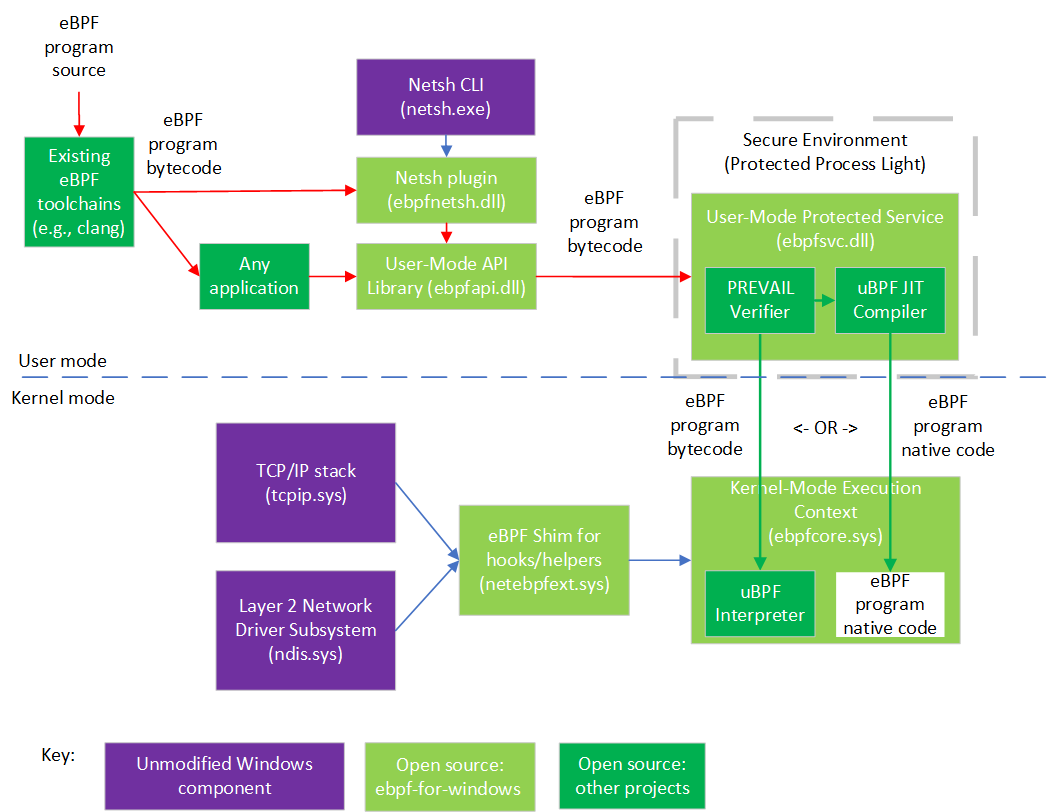
The following diagram shows the architecture of this project and related components:
As shown in the diagram, existing eBPF toolchains (clang, etc.) can be used to generate eBPF bytecode from source code in various languages. Bytecode can be consumed by any application, or via the Netsh command line tool, which use a shared library that exposes APIs (intended to match Libbpf APIs plus some additions, though this is still in progress).
The eBPF bytecode is sent to a static verifier (the PREVAIL verifier) that is hosted in a user-mode protected process (a Windows security environment that allows a kernel component to trust a user-mode daemon signed by a key that it trusts). If the bytecode passes all the verifier checks, it can be either loaded into an interpreter (from uBPF in the kernel-mode execution context, or JIT compiled (via the uBPF JIT compiler) and have native code load into the kernel-mode execution context (but see the FAQ at bottom about HVCI).
Temporary Note: some parts are still under development and may not appear when building the master branch, but the end-to-end functionality can still be tested immediately while the security hardening is still in progress.
eBPF programs installed into the kernel-mode execution context can attach to various hooks (currently two hooks so far: XDP and a socket bind hook) and call various helper APIs exposed by the eBPF shim, which internally wraps public Windows kernel APIs, allowing the use of eBPF on existing versions of Windows. More hooks and helpers will be added over time.
Getting Started
This project supports eBPF on Windows 10, and on Windows Server 2016 or later. To try out this project, see our Getting Started Guide.
Want to help? We welcome contributions! See our Contributing guidelines.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Is this a fork of eBPF?
No.
The eBPF for Windows project leverages existing permissive licensed projects, including uBPF and the PREVAIL verifier, running them on top of Windows by adding the Windows-specific hosting environment for that code. Similarly, it provides Windows-specific hooks and helpers, along with non-GPL'ed hooks/helpers that are common across Linux, Windows, and other platforms.
The Linux kernel contains an eBPF execution environment, hooks, helpers, a JIT compiler, verifier, interpreter, etc. that is GPL licensed and so cannot be used for purposes that require a more permissive license.
For that reason, there are already various projects in the eBPF community that have permissive licenses, such as:
- the IOVisor uBPF project,
- the PREVAIL verifier,
- Libbpf APIs, and
- the generic-ebpf project, among others.
2. Does this provide app compatibility with eBPF programs written for Linux?
The intent is to provide source code compatibility for code that uses permissively licensed hooks and helpers.
Linux provides many hooks and helpers, some of which are GPL-licensed but some are more permissively licensed. The GPL-licensed hooks and helpers tend to be very Linux specific (e.g., using Linux internal data structs) that would not be applicable to other platforms anyway, including other platforms supported by the generic-ebpf project. The hooks and helpers that can be used with a permissive license tend to be generically applicable and those will be supported.
Similarly, the eBPF for Windows project supports Libbpf APIs to provide source code compatibility for applications that interact with eBPF programs.
3. Will eBPF work with HyperVisor-enforced Code Integrity (HVCI)?
eBPF programs can be run either in an interpreter or natively using a JIT compiler.
HyperVisor-enforced Code Integrity (HVCI) is a mechanism whereby a hypervisor, such as Hyper-V, uses hardware virtualization to protect kernel-mode processes against the injection and execution of malicious or unverified code. Code integrity validation is performed in a secure environment that is resistant to attack from malicious software, and page permissions for kernel mode are set and maintained by the hypervisor.
Since a hypervisor doing such code integrity checks will refuse to accept code pages that aren't signed by a key that the hypervisor trusts, this does impact eBPF programs running natively. As such, when HVCI is enabled, eBPF programs work fine in interpreted mode, but not when using JIT compilation, regardless of whether one is using Linux or Windows.