Signed-off-by: Gergő Rubint <gergo@grubint.com> Signed-off-by: Gergő Rubint <gergo@grubint.com> |
||
|---|---|---|
| .. | ||
| .devcontainer | ||
| .vscode | ||
| test-project | ||
| .npmignore | ||
| README.md | ||
README.md
Azure Terraform (Community)
build, change, and version Azure infrastructure with terraform
Summary
Terraform is an open-source tool that provides the ability to build, change, and version infrastructure as code using declarative configuration files with HashiCorp Configuration Language (HCL).
This recipe allows you to get going quickly with Terraform in Azure. Includes Terraform, the Azure CLI, the Docker CLI (for testing locally), Node.js for Cloud Shell, and related extensions and dependencies.
| Metadata | Value |
|---|---|
| Contributors | Carlos Mendible, Charles Zipp, Lila Molyva, Tas Devani |
| Categories | Community, Azure, Other |
| Definition type | Dockerfile |
| Supported architecture(s) | x86-64, arm64/aarch64 for bullseye based images |
| Works in Codespaces | Yes |
| Container host OS support | Linux, macOS, Windows |
| Container OS | Debian |
| Languages, platforms | Azure, Terraform |
Using this definition
While technically optional, this definition includes the Azure Terraform extension which requires a few pre-requisites:
- Azure Subscription: A current Azure subscription or a free trial account needed.
You can also choose the specific version of Terraform installed by updating the following line in .devcontainer/devcontainer.json:
"arg": {
"TERRAFORM_VERSION": "0.14.5"
"TFLINT_VERSION": "0.24.1",
"TERRAGRUNT_VERSION": "0.28.1"
"INSTALL_AZURE_CLI": "true",
"INSTALL_DOCKER": "true",
"NODE_VERSION": "lts"
}
If you plan to use the Azure Cloud Shell for all of your Terraform operations, you can set "INSTALL_DOCKER": "false". Conversely, if you do not plan to use Cloud Shell, you can set "NODE_VERSION": "none". By default, both are installed so you can decide later.
Beyond git, this Dockerfile includes zsh, Oh My Zsh!, a non-root vscode user with sudo access, and a set of common dependencies for development.
Adding the definition to a project or codespace
-
If this is your first time using a development container, please see getting started information on setting up Remote-Containers or creating a codespace using GitHub Codespaces.
-
Start VS Code and open your project folder or connect to a codespace.
-
Press F1 select and Add Development Container Configuration Files... command for Remote-Containers or Codespaces.
Note: If needed, you can drag-and-drop the
.devcontainerfolder from this sub-folder in a locally cloned copy of this repository into the VS Code file explorer instead of using the command. -
Select this definition. You may also need to select Show All Definitions... for it to appear.
-
Finally, press F1 and run Remote-Containers: Reopen Folder in Container or Codespaces: Rebuild Container to start using the definition.
Testing the Definition
This definition includes some test code that will help you verify it is working as expected on your system. Follow these steps:
-
Follow steps 1-4 from the above section.
-
Fill in the values for the environment variables in the
.devcontainer/devcontainer.envfile- This file allows customization of the environment variables and the values needed for the terraform tasks.
-
Open the Command Palette with
Ctrl/CMD+Shift+Por press F1 and run Remote-Containers: Reopen Folder in Container to start using the definition. -
VS Code tasks have been configured to run commonly used Terraform commands. The
test-projectfolder includes a Terraform template that provisions a new Azure Resource Group and the commands can be run viaCtrl/CMD+Shift+P>Tasks: Run Tasks.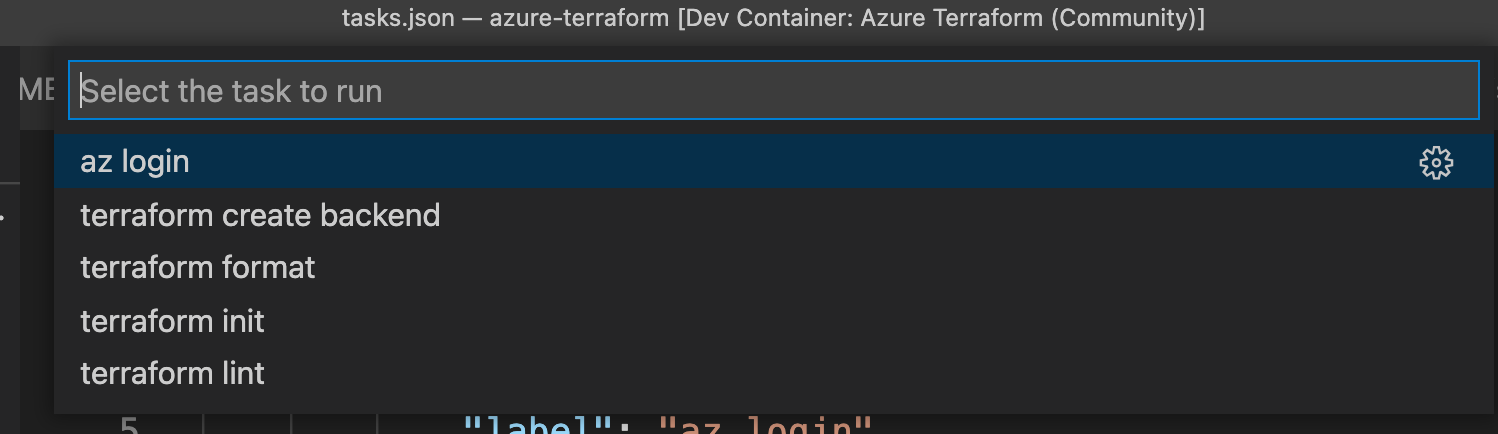
A more detailed explanation of the tasks can be found in the next section.
Running the Tasks
Once the environment settings are configured with the .devcontainer/devcontainer.env, you can begin executing terraform commands. VS Code tasks have been configured to run each of the commonly used terraform commands.
az login: login to Azure and set your default subscriptionterraform create backend: create (if it does not exists) a remote azurerm backend (storage account)terraform init: installs plugins and connect to terraform remote backendterraform format: fix formatting issuesterraform lint: fix linting issues
For additional terraform commands, you can use the Azure Terraform extension.
- Navigate to the directory where the templates are located (
test-project/templates) - Open the Command Palette with
Ctrl/CMD+Shift+Por press F1 and run the following:Azure Terraform: Validate: check templates for syntax errorsAzure Terraform: Plan: report what would be done with apply without actually deploying any resourcesAzure Terraform: Apply: deploy the terraform templatesAzure Terraform: Destroy: destroy resources deployed with the templates
For a complete list of all the available commands as part of the Azure Terraform extension, please visit this page
References
- Terraform Overview
- Terraform Tutorials
- Terraform with Azure
- Terraform Extension
- Azure Terraform Extension
License
Copyright (c) Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved.
Licensed under the MIT License. See LICENSE.