|
|
||
|---|---|---|
| build | ||
| src | ||
| test | ||
| .editorconfig | ||
| .gitattributes | ||
| .gitignore | ||
| GitInfo.txt | ||
| LICENSE | ||
| NuGet.Config | ||
| README.md | ||
| build.cmd | ||
| build.proj | ||
| build.yml | ||
README.md
Xamarin.VSSDK
Extensions to the Visual Studio SDK to make extensions authoring easier.
Installation
For libraries that will be consumed by a VSIX project:
install-package Xamarin.VSSDK
For the VSIX project itself:
install-package Xamarin.VSSDK.BuildTools
Usage
The XVSSDK (Xamarin.VSSDK) is intended for SDK-style VSIX projects that will target (or be used in) more than one version of Visual Studio.
This is achieved by leveraging the SDK-style projects' support for multi-targeting via the new
TargetFrameworks property.
The XVSSDK will perform the following mapping of VS versions:
| TargetFramework | Visual Studio Version |
|---|---|
| net46 | 2013 |
| net461 | 2015 |
| net462 | 2017 |
The XVSSDK automatically adds TF-specific dependencies on the VSSDK_Reference_Assemblies nuget package,
which provides all the necessary APIs to author VS extensions.
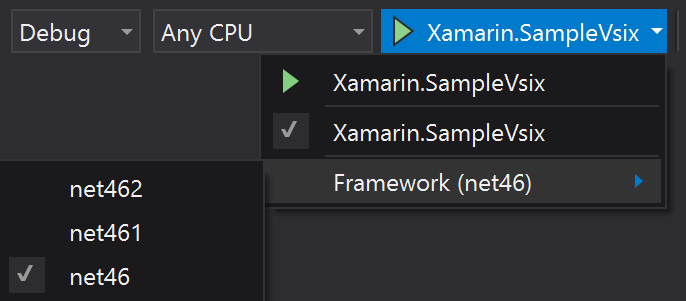
When using VS2017 Update 3 or greater (15.3+), you can also select the target Visual Studio version by selecting the relevant Target Framework from the Run dropdown:
When doing so, the TargetFramework will be set to the selected one, causing the right VSSDK BuildTools
package to be used to deploy the extension to the right Experimental Instance. So you can use VS2017 to
target and debug an extension in VS2015 Experimental Instance.
NOTE: the selected target framework is persisted in the .user options file, with the
ActiveDebugFrameworkproperty name
If no ActiveDebugFramework is selected, the XVSSDK will automatically target the current Visual Studio version,
which is the most common scenario.
Multi-Targeting
When targeting multiple Visual Studio versions, there are two main scenarios you might want to achieve:
- Single VSIX for all targeted Visual Studio versions
- One VSIX per targeted Visual Studio version
Single VSIX for multiple Visual Studio versions
In this case, you should always build the final VSIX using the newest VSSDK Build Tools. This ensures that
the newest VSIXInstaller.exe can properly install the extension to all supported Visual Studio versions.
During development (IDE builds), the automatic switching of Build Tools behavior described above works great, but for CI/command line/release builds, it's not quite what you need.
In order to do that, you need to explicitly take a dependency on the latest VSSDK Build Tools nuget package for non-IDE builds. CI and command line (after a restore) will properly reference the latest tools automatically and override the per-target framework dependency that XVSSDK sets up:
<ItemGroup>
<PackageReference Include="Microsoft.VSSDK.BuildTools" Version="15.0.26201" Condition="'$(BuildingInsideVisualStudio)' != 'true'" />
</ItemGroup>
One VSIX per Visual Studio version
When building a VSIX that will only be installed in a specific version of Visual Studio (i.e. you depend on APIs that are specific to each version), it's best to actually build for each with the build tools for that particular IDE.
Multi-targeting is very useful when the code (or references) are different across the targeted frameworks. It doesn't work quite as well when the actual targets and tasks need to change, since MSBuild can't unload the build tasks used in the first target framework when the subsequent one runs (i.e. loading build tools for VS2013 for net46, then building for VS2015 for net461 with a different Build Tools tasks).
Therefore, when multi-targeting, you need to build for each target IDE separately. This can be achieved
easily by passing a /p:Dev=[12.0,14.0,15.0]. We use the Dev property instead of passing /p:TargetFramework
because the latter can affect the build for other projects that don't require changing the target framework.
By using our own property, which is used to change TargetFramework just for the VSIX projects, we achieve
the same goal without disrupting other projects.