11 KiB
Contributor Onboarding
Thank you for taking the time to contribute to Azure Functions in Java
This project has adopted the Microsoft Open Source Code of Conduct. For more information see the Code of Conduct FAQ or contact opencode@microsoft.com with any additional questions or comments.
Table of Contents
- Contributor Onboarding
What should I know before I get started
Pre-requisites
- OS
- MacOS, Ubuntu (or) Windows10
- IDE
- Java Tools
- Maven
- JDK (Azul Zulu for Azure) 8 - this also installs Java 1.8 JRE
- Azure Tools
- Azure Storage Emulator (or) Create a storage account in Azure
- Azure Functions Core Tools v2.7.x and above.
- Azure Storage Explorer
Pull Request Change flow
The general flow for making a change to the library is:
- 🍴 Fork the worker repo (add the fork via
git remote add me <clone url here> - 🌳 Create a branch for your change (generally branch from dev) (
git checkout -b my-change) - 🛠 Make your change
- ✔️ Test your change
- ⬆️ Push your changes to your fork (
git push my-change) - 💌 Open a PR to the dev branch. Repo owner will run the current CI pipeline.
- 📢 Address feedback and make sure tests pass (yes even if it's an "unrelated" test failure)
- 📦 Rebase your changes into meaningful commits (
git rebase -i HEAD~NwhereNis commits you want to squash) - :shipit: Rebase and merge (This will be done for you if you don't have contributor access)
- ✂️ Delete your branch (optional)
Development Setup
Visual Studio Code Extensions
The following extensions should be installed if using Visual Studio Code for debugging:
- Java debugging for Visual Studio Code (Java for VSCode extension)
- Azure Functions Extensions for Visual Studio Code v0.19.1 and above.
Setting up the end-to-end development environment
The following steps outline an end to end development environment to enable developers to debug all the way from the Azure Functions Host to the Java Worker when a Java Azure Function is invoked:
-
Use any Java Azure Function starter sample and run
mvn clean packageto produce the target executable of a Java Azure Function. -
Git clone the Azure function host code base open it using your favorite IDE.
-
Navigate to
WebJobs.Script.WebHostproject -
Right click on
WebJobs.Script.WebHostproject and add the following environment variables into your debugging configuration:Variable Value FUNCTIONS_WORKER_RUNTIME java languageWorkers:java:arguments -agentlib:jdwp=transport=dt_socket,server=y,suspend=n,address=5005 AZURE_FUNCTIONS_ENVIRONMENT Development AzureWebJobsScriptRoot a path to your azure function target folder from step 1,i.e. ~/< your-folder-path >/target/azure-functions/<azure-function-name-####> Notes
- In macOS, you might need to add JAVA_HOME as a debugging environment variable.
- If using Visual Studio Code, then add these environment variables in the launch.json in the
envobject underconfigurations.
Here is a sample configuration for Visual Studio Code
"env" : { "JAVA_HOME" : "/Library/Java/JavaVirtualMachines/zulu-8.jdk/Contents/Home", "FUNCTIONS_WORKER_RUNTIME":"java", "languageWorkers:java:arguments": "-agentlib:jdwp=transport=dt_socket,server=y,suspend=n,address=5005", "AZURE_FUNCTIONS_ENVIRONMENT": "Development", "AzureWebJobsScriptRoot" : "<path_to_java_function>/java-functions-di/java-starter/functions-di/target/azure-functions/functions-di-20201102134253063" }- Also add the following in the tasks.json file to point to your azure functions folder. Here is a sample tasks.json file
{ "version": "2.0.0", "tasks": [ { "label": "build", "command": "dotnet", "type": "process", "args": [ "build", "<path_to_host_cloned_repo>/azure-functions-host/src/WebJobs.Script.WebHost/WebJobs.Script.WebHost.csproj", "/property:GenerateFullPaths=true", "/consoleloggerparameters:NoSummary" ], "problemMatcher": "$msCompile" }, { "type": "func", "command": "host start", "problemMatcher": "$func-watch", "isBackground": true, "options": { "cwd": "<path_to_java_function>/java-functions-di/java-starter/functions-di/target/azure-functions/functions-di-20201102134253063" } } ] } -
Navigate to
azure-functions-host/src/WebJobs.Script/Workers/ProcessManagement/WorkerProcess.csclass and add breakpoint at_process.Start().Note: Make sure that WebJobs.Script.WebHost is set as a Startup Project
-
Now in another IDE instance, git clone your fork for azure function worker and open it.
-
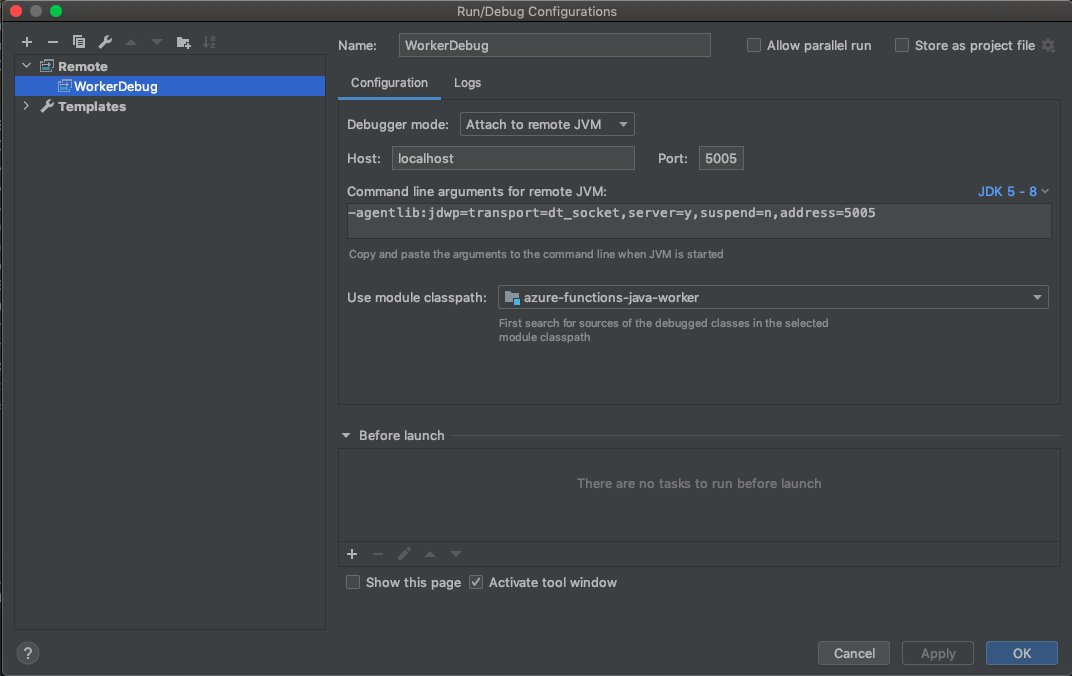
Add new remote debugging configuration.
Here is a sample configuration for IntelliJ IDEA
With this you have completed the setup for Azure Functions Host and the Azure Functions Java Worker Development.
Start Debugging
-
Run the azure-functions-host from Step 5 in debugging mode (.NET Core Launch Debug). Wait until it stops at the
_process.Start()breakpoint. At this point, the host is started and the java language worker needs to connect to the host. -
Navigate to
azure-functions-java-worker/src/main/java/com/microsoft/azure/functions/worker/JavaWorkerClient.javaand add a breakpoint in the constructor. Click the Remote Debugging configured in Step 7. This connects the worker process to the host and runs worker in debugging mode. -
Run through the breakpoint in the host until it hits the breakpoint in
JavaWorkerClient.java. At this point the worker and host are up and running with your function app (this was configured as part of the environment variables above) -
Open a browser and invoke the HTTP Trigger and it will reach the
executemethod inazure-functions-java-worker/src/main/java/com/microsoft/azure/functions/worker/broker/JavaMethodExecutorImpl.javaand can then follow along the execution of the function from here.
Testing a new version of the Java Worker
-
In case you need to test a new version from Java worker code, you'll need to:
-
Compile the worker
mvn clean package -Dmaven.javadoc.skip=true -Dmaven.test.skip -Dorg.slf4j.simpleLogger.log.org.apache.maven.cli.transfer.Slf4jMavenTransferListener=warn -B -
Navigate to target folder and rename
azure-functions-java-worker-1.8.0.jartoazure-functions-java-worker.jar -
Copy the jar file to the debug folder in the host code base(<Azure_Function_Host_Path>/azure-functions-host/src/WebJobs.Script.WebHost/bin/Debug/netcoreapp3.1/workers/java)
-
Restart host debugger
-
App settings
You can run your local function app in two ways:
- By running the host code and worker code
- By running core tools
If you are running the host code and worker code to debug your function app, then you need to add the app settings as part of the host's environment variables (in launch.json).
If you are running core tools to debug your function app, then you need to add the app settings in your function app's local.settings.json file.
Common Issues
Extension Bundle
If you are running the host code and worker code to debug your function app, the extension bundle does not need to be enabled if your local function app only uses the HTTP trigger. However, it does need to be enabled when using other types of triggers and output bindings (e.g. EventHub). Otherwise, you will get exceptions like "The binding type(s) were not found in the configured extension bundle. Please ensure the type is correct and the correct version of extension bundle is configured". In order to enable the extension bundle, you need to follow the steps here:
https://github.com/Azure/azure-functions-host/wiki#extension-bundle-configuration
The downloadPath attribute can be any path in your local machine and is used to indicate what directory you would like some generated files to be saved.
This is a sample host.json file configuration in the function app:
{
"version": "2.0",
"extensionBundle": {
"id": "Microsoft.Azure.Functions.ExtensionBundle",
"version": "[4.*, 5.0.0)",
"downloadPath": "C:/Users/<user>/Repos"
}
}
If you are running core tools to debug your function app, you do not need to enable the extension bundle.
Running unit tests
- Add your unit tests under ./src/test folder
- Run:
mvn clean package
Getting help
- Leave comments on your PR and @username for attention
Requesting a release
- If you need a release into maven central, request it by raising an issue and tagging @TsuyoshiUshio and @amamounelsayed