18 KiB
Contribute to Terraform AzureRM provider
This document describe how you can get ready to contribute to the AzureRM Terraform provider. We also recommend that you read the README on the AzureRM Terraform Provider repository.
Setup your system
Terraform
You need to install Terraform on your dev environment. You can downlaod it from terraform.
Go tools
Terraform is developed using Go Programming Language. You need to install Go Programming Language 1.x.x to be able to build and debug the provider locally. You can check to see what version of Go is currently being used in the project by checking the go.mod file in the root directory. You can download it from golang and find the installation instructions for your system golang install
Then you can test your environment following the instructions on golang testing.
Check your environment variables
As with many Go project, AzureRM Terraform provider rely on your GOPATH environment variable. You may want to make sure it is well configured for your system, reading golang setting go path.
Visual Studio Code
You can use the IDE you love, but in this documentation we will describe how to contribute to the Terraform AzureRM provider using Visual Studio Code. You can download it for your system from visual studio.
Once installed, download the Go extension for VS Code:
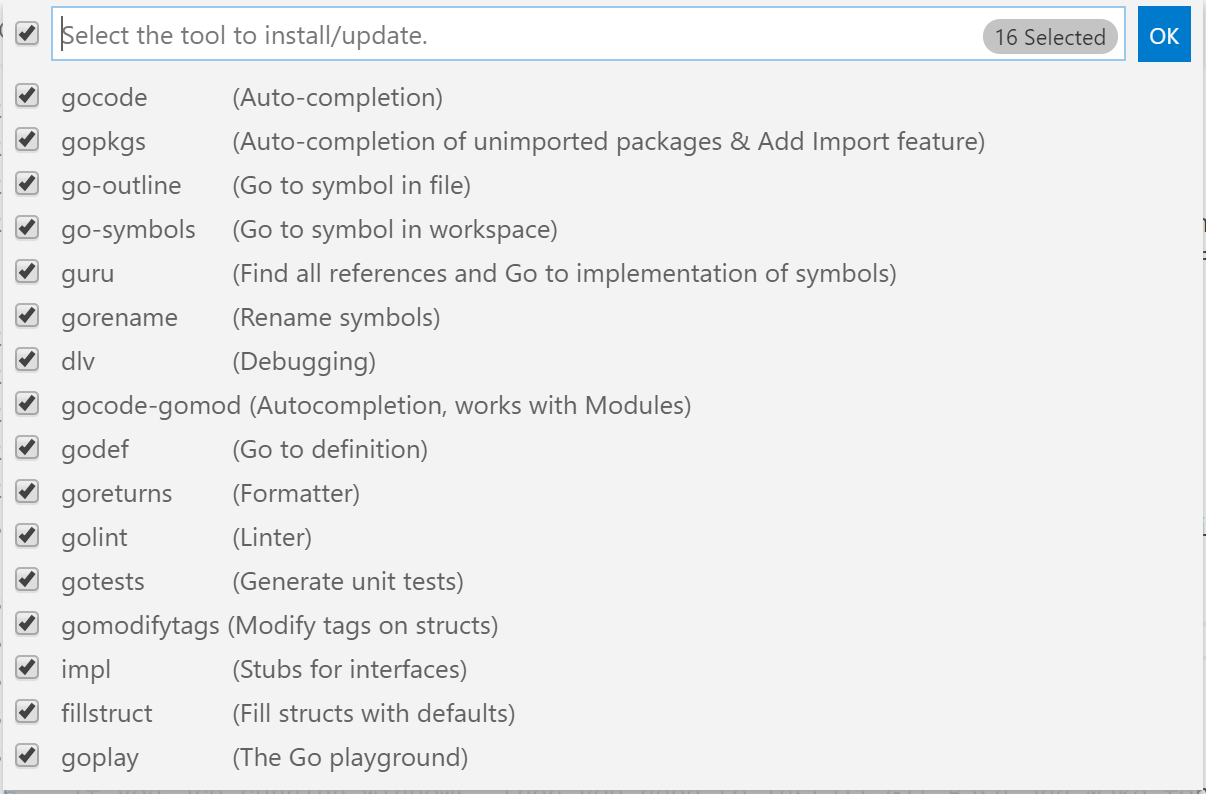
Once installed, open VS Code and look for the Go: Install/Update Tools in the command palette, a select all the tools:
Specific requirements for Windows users
If you are running Windows, then you need to install Git Bash and Make for Windows. Check the dedicated section on Terraform on Azure repository terraform developer requirements.
Get the sources
First, go to the AzureRM Terraform provider project page and fork the repository into your GitHub account.
As the provider uses go modules, you can clone the repository in any path.
Build the sources
You can check that everything is OK by building the AzureRM provider:
cd $GOPATH/src/github.com/terraform-providers/terraform-provider-azurerm
make build
Once completed, the binary of the AzureRM provider should be available in the $GOPATH/bin directory.
Note: on Windows, you need to use Git Bash
More information here.
Work with your local build
Once you have built a new version of the AzureRM Terraform provider, you can use it locally.
First, you need to move your terraform binary which is in the $GOPATH/bin folder on your machine, to the third-party plugins folder which is located at ~/.terraform.d/plugins on most operating systems and %APPDATA%\terraform.d\plugins on Windows.
Then you will need to go to your terraform test folder where the main.tf configuration file exists and initialize your terraform working directory by using the terraform init command.
If the third-party plugin folder is empty, the init operation will download the AzureRM Provider for you.
More information here.
terraform init will look for the providers in the folder where the .tf files are located, so it is possible to just copy the provider from $GOPATH/bin to your current folder and it will be used instead of getting downloaded.
Debug the AzureRM provider using Visual Studio Code and Delve
It is possible to use Visual Studio Code and Delve (the Golang debugger) to debug the AzureRM provider. The easiest way to debug Terraform AzureRM Provider is to execute the acceptances unit test with the Delve debugger attached. Acceptance tests are tests that are written for every resources and data sources and that will really execute the code to an Azure subscription, to validate everything is working well.
First, to be able to connect to Azure, you need to create a service principal using the following command:
az ad sp create-for-rbac --role=Contributor --scope=/subscriptions/<YOUR_SUBSCRIPTION_ID>
Then, you need to create a .launch.json file inside the .vscode folder at the root of the Terraform AzureRM provider directory (create the .vscode folder if it does not exist).
Copy the following content into the file:
{
// Use IntelliSense to learn about possible attributes.
// Hover to view descriptions of existing attributes.
// For more information, visit: https://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?linkid=830387
"version": "0.2.0",
"configurations": [
{
"name": "Launch test function",
"type": "go",
"request": "launch",
"mode": "test",
"program": "${workspaceRoot}/azurerm/resource_arm_container_registry_test.go",
"args": [
"-test.v",
"-test.run",
"TestAccAzureRMContainerRegistry_geoReplication"
],
"envFile": "${workspaceRoot}/.vscode/private.env",
"showLog": true
},
]
}
The configuration above allows to start debugging a Terraform resource, by launching one or more acceptance test:
- The
programproperty indicates the file you want to debug - The last entry of the
argsproperty, hereTestAccAzureRMContainerRegistry_geoReplicationrepresents th test to launch. You can use regex to run multiple tests (ex:TestAccAzureRMContainerRegistry_*) - The
envFileproperty defines the path to get the environment variables file (mainly Azure credentials) that needs to be used to run the acceptance test.
Create the private.env file into the .vscode folder and fill it with the following environment variables:
ARM_CLIENT_ID=<YOUR_SERVICE_PRINCIPAL_CLIENT_ID>
ARM_CLIENT_SECRET=<YOUR_SERVICE_PRINCIPAL_CLIENT_SECRET>
ARM_SUBSCRIPTION_ID=<YOUR_AZURE_SUBSCRIPTION_ID>
ARM_TENANT_ID=<YOUR_AZURE_TENANT_ID>
ARM_TEST_LOCATION=<AZURE_LOCATION_1>
ARM_TEST_LOCATION_ALT=<AZURE_LOCATION_2>
TF_ACC=1
If you would preffer to use the UI to launch the tests, it is aso possible to specify the environment variables used by vscode integrated testing by modifying the settings.json. Two options are available
- Use the built in variables definition:
"go.testEnvVars": {
"ARM_CLIENT_ID" : "<YOUR_SERVICE_PRINCIPAL_CLIENT_ID>"
...
...
},
- Use the contents of a file as
private.env
"go.testEnvFile": "${workspaceRoot}/.vscode/private.env"
Note: it is possible to customize the logging level of Terraform. It might be super useful in some situations. It can be done by setting the TF_LOG environment variable. Refer to the official debugging documentation for more details.
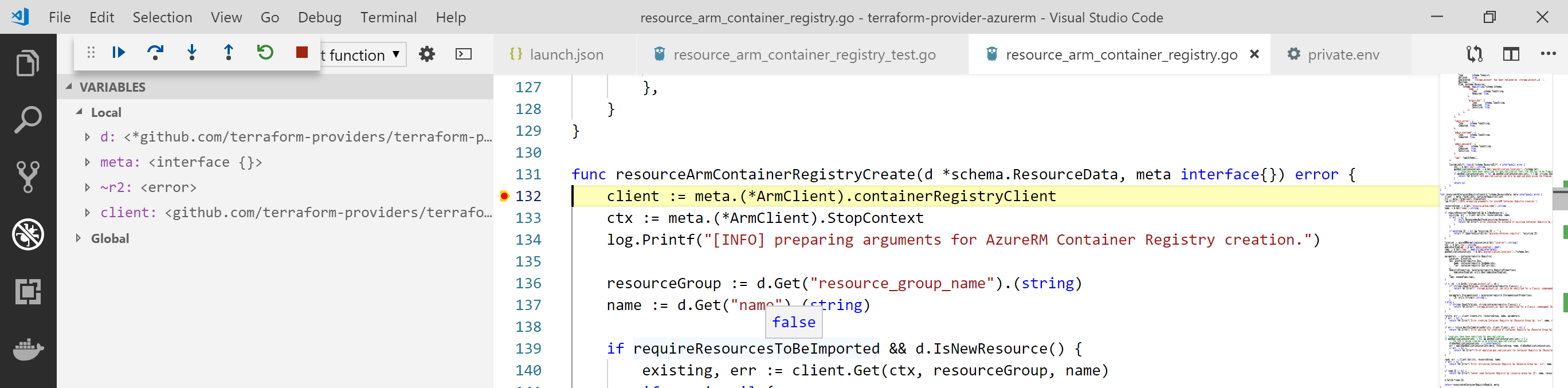
Once done, you can just press F5 and the debug will start! You can place breakpoints in your code to do step by step debugging:
Note: the first time your start the debug, it can take a while, you need to be patient :-)
How to contribute to the Azure RM provider
Note: we also invite you to read the official documentation about developing a provider here
First you need to pick an issue on the provider by commenting the issue and saying that you're going to work on that, to make sure that the repo maintainers are aware that you are going to work on this issue. We also strongly advise that you describe the work you are planning to do, like explaining your implementation, submitting the TF schema for new resources, to make sure the discussion start early as possible with the reviewers.
Note: if there is no issue for the problem you are trying to solve, you can create one.
If you are a new contributor, there is a good first issue label that may help you to filter the issue and start with a simple one.
For each piece of code that you write into the provider, you need to make sure that you have:
- the implementations of the
data sourceand/orresourcedefinition - acceptance test created or updated
- documentation created or updated
- example created or updated (optional)
Data sources, resources and tests are defined in the azurerm/internal/services folder of the repository.
Documentation for data sources is in the website/docs/d folder and documentation for resources is in the website/docs/r folder.
Finally, examples are located in the examples folder.
AzureRM Terraform provider uses the Azure SDK for Go to interact with Azure. It's important that you respect that rule. If you are trying to do something that is not available in the Azure SDK for Go, then you should check if the API is availble in Azure Service Repository and open an issue in the Azure SDK for Go repository to have it added to a future release of the Azure SDK for Go.
We recommand that you start with fixing issues/patching an existing data source or resource to understand how it works in details before trying to implement a brand new one.
Don't forget that you are working on your own fork of the repository and that you need to open a pull request to the main repository to bring your update to the HashiCorp team, for review.
Working with Azure SDK for Go
All the imports for the Azure for Go SDK services have to be done in the client.go file. It exposes a top level struct, Client that exposes all the service clients that you may use in a data source or resource to interact with Azure. If the service already exist and you are just modifying an existing resource you can skip this step.
Then you need to register your subservice in client.go in your corresponding service folder.
For example, if you need to work on implementing Azure Batch Account support to the provider:
- Check if the service
Batchregistered in service client.go. If not, you need to register your service. - Go to your corresponding service folder batch and write a
client.goin client folder. If the service folder does not exist, you will need to create one. - Add a variable
AccountClientwhich is created by the service apiNewAccountClientWithBaseURIfrom"github.com/Azure/azure-sdk-for-go/services/batch/mgmt/2019-08-01/batch".
type Client struct {
AccountClient *batch.AccountClient
}
- Register your client in the Terraform ResourceManagerAuthorizer:
func NewClient(o *common.ClientOptions) *Client {
accountClient := batch.NewAccountClientWithBaseURI(o.ResourceManagerEndpoint, o.SubscriptionId)
o.ConfigureClient(&accountClient.Client, o.ResourceManagerAuthorizer)
return &Client{
AccountClient: &accountClient,
}
}
By doing the four steps above, you will make sure that when developping the data source or the resource, you can access the Azure SDK for Go clients that you need.
Developing a Data Source
When naming a new data source file it should follow the below naming convention: name_of_the_data_source_data_source.go
A data source is composed of two relevant functions:
- The function that creates a
schema.Resourceobject that returns the schema (definition) of the data source,i.e. the property that compose the data source, and some rules about those properties. You only need to provide required properties to locate that resource, and mark all other properties returned from the service asComputed. This function is named by convention dataSourceArmNAME_OF_THE_DATA_SOURCE, for exampledataSourceArmBatchAccountfor a Batch Account. - The function that retrieves the data from Azure using the Azure SDK for Go client and set all the values related to the data source. This function is named by convention dataSourceArmNAME_OF_THE_DATA_SOURCERead, for example
dataSourceArmBatchAccountReadfor a Batch Account.
This function takes a schema.ResourceData in parameter. You can get the name of the object to retrieve and any property that is defined by the user on that object:
resourceGroup := d.Get("resource_group_name").(string)
name := d.Get("name").(string)
You can get a reference on any Azure SDK for Go client registered in the client.go using:
client := meta.(*clients.Client).Batch.AccountClient
Finally, you can set values retrieve from Azure on the same object, using the Set function:
d.Set("account_endpoint", resp.AccountEndpoint)
You can check the whole definition of the Azure Batch Account data source here.
Once your data source is defined, you need to register it into the data sources map in the registration.go file:
func (r Registration) SupportedDataSources() map[string]*schema.Resource {
return map[string]*schema.Resource{
"azurerm_batch_account": dataSourceArmBatchAccount(),
}
}
Developing a resource
Developing a resource is really similar to developing a data source. Instead of having only a function to read the data from Azure, it also offers the possibility to write functions to create, update and delete the resource. Apart from that, concepts are the same:
- The file is named using the convention: name_of_resource_resource.go
- One function to define the schema of the resource, named by convention resourceArmNAME_OF_RESOURCE, for example
resourceArmBatchAccount. - One function to create the resource, named by convention resourceArmNAME_OF_RESOURCECreate, for example
resourceArmBatchAccountCreate. - One function to read the resource, named by convention resourceArmNAME_OF_RESOURCERead, for example
resourceArmBatchAccountRead. - One function to update the resource, named by convention resourceArmNAME_OF_RESOURCEUpdate, for example
resourceArmBatchAccountUpdate. - One function to delete the resource, named by convention resourceArmNAME_OF_RESOURCEDelete, for example
resourceArmBatchAccountDelete.
The Azure Batch Account resource is a good and simple example to understand the flow.
Once your resource is defined, you need to register it into the resources map in the registration.go file:
func (r Registration) SupportedResources() map[string]*schema.Resource {
return map[string]*schema.Resource{
"azurerm_batch_account": resourceArmBatchAccount(),
}
}
Acceptance tests
Acceptance tests are tests that will run live on your Azure subscription to validate that your resource/data source is working as expected. Each resource/data source should have its own set of acceptance tests that will run independently of each other.
All tests for a given resource/data source are located in the test folder which is a sub folder of the service folder. The file name for the tests will be exactly the same as the resource/data source with the addition of the _test.go suffix. For example, if you created a data source for batch account, the data source file would be named batch_account_data_source.go and the test file would have the name batch_account_data_source_test.go.
You can find examples of tests for Azure Batch Account data source here and Azure Batch Account resource here.
Please refer to the above section to learn how to run the acceptance tests on your computer.