9.5 KiB
| title | description | slug | res_type |
|---|---|---|---|
| Composer Tab | Learn how to use the Composer tab in the Fiddler Everywhere web-debugging HTTP-proxy client. | composer-tab | kb |
The Composer tab enables you to manually create a new HTTP or HTTPS request from scratch and edit an existing captured request, as well as send and test them. This article explains the user interface that creates the Fiddler Everywhere's Composer. [Learn more about how to use the Composer here...]({%slug composer-get-started%})
To get started, open the Composer tab from the same pane. Alternatively, you can open a new Composer tab by clicking the New Request (+) button in the [Requests]({%slug saved-requests-tab%}) tab or by using the Edit in Composer option from the Live Traffic grid's context menu.
The Composer tab houses the Request Composer and the Request Inspector, and contains major sections to construct a request, to observe the response, and to save, replay and share previously composed requests.
The top section contains a toolbar with the following functionalities:
- The HTTP Methods is a drop-down where you can specify the request method—for example, GET, POST, and so on.
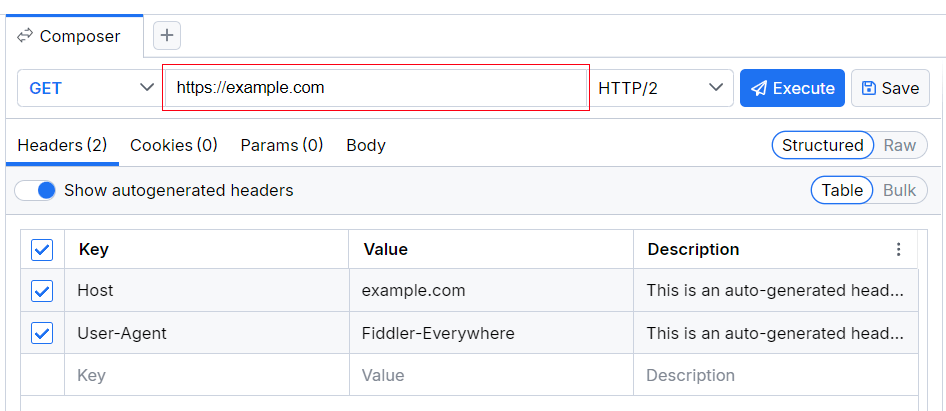
- The URL field enables you to enter the endpoint URL.
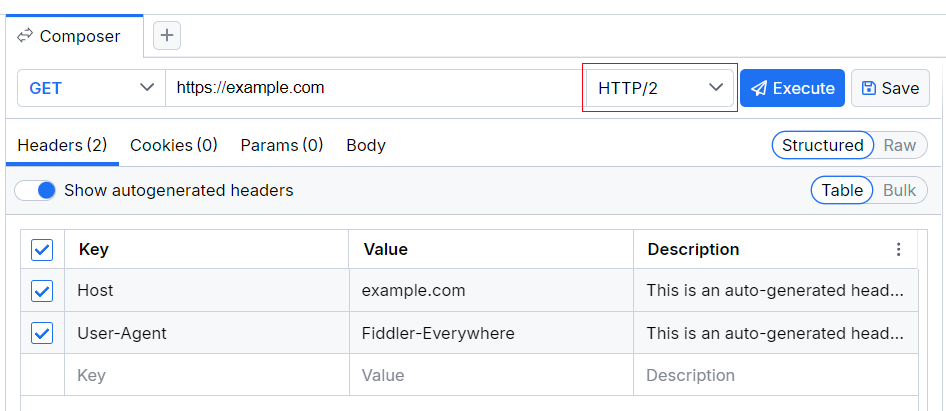
- The HTTP version is a drop-down where you can select the HTTP version. By default, the selected version is HTTP 1.1.
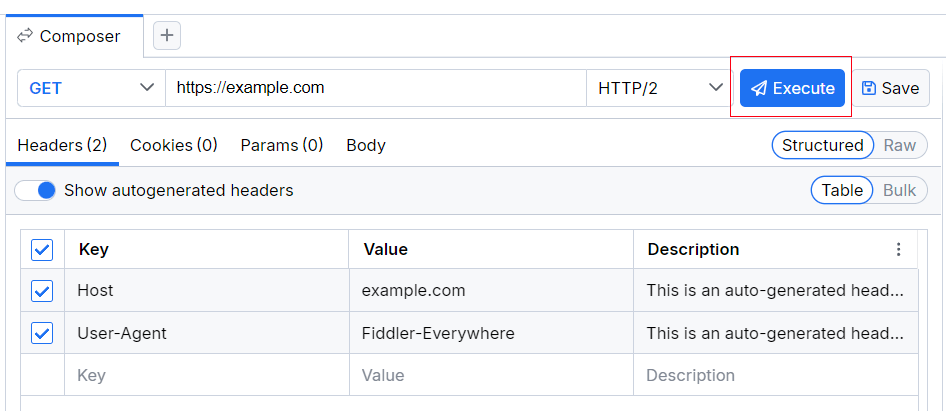
- The Execute button is an action button for executing the composed request.
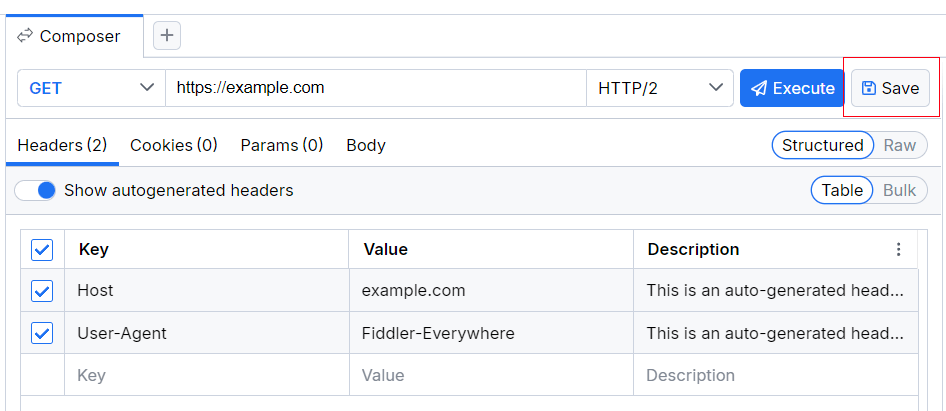
- The Save button enables you to save your composed request in the [Requests]({%slug saved-requests-tab%}) list.
The mid-section provides options to further modify your request through the following options:
- The Headers section allows you to add and modify the HTTP headers of the request.
- The Cookies section allows you to add and modify cookies.
- The Params section allows you to add and modify the request parameters.
- The Body section allows you to modify the request body and supports various formats such as JSON, form-data, XML, text, and more.
The bottom section is a response inspector, which shows the response from the executed request.
In the Requests list to the left you can save the composed request for later usage. From the Requests list, you can share the entry of saved requests with collaborators.
By default, the Composer automatically adds headers like User-Agent, Host, and Content-Length so that the HTTPS request is sent correctly. You can remove the default User-Agent header but note that this may break the composition of a secure (HTTPS) request.
HTTP Methods
The Composer supports the creation of a request with the following HTTP methods:
- GET—Requests a representation of the specified resource. Requests using GET have to retrieve data only.
- PUT—Replaces all current representations of the target resource with the request payload.
- POST—Submits an entity to the specified resource, often causing a change in the state or side effects on the server.
- DELETE—Deletes the specified resource.
- HEAD—Asks for a response identical to a GET request, but without the response body.
- TRACE—Performs a message loop-back test along the path to the target resource.
- SEARCH—Used by a client to ask the server to perform a query operation, described by the request payload, over a set of data scoped to the effective request Uniform Resource Identifier (URI).
- PROPFIND—Retrieves properties defined on the resource and identified by the Request-URI.
- PATCH—Applies partial modifications to a resource.
- MKCOL—You can include the method in the scope of a transaction by submitting a Transaction Header with a lock token that corresponds to that transaction.
- MOVE—Used to move a resource to the location that is specified by a request URI.
- LOCK—Used to take out a lock of any access type on a resource so that another principal will not modify the resource while it is being edited.
- UNLOCK—Used to remove the lock on the resource at the request URI.
- OPTIONS—Used to describe the communication options for the target resource.
URL Field
The URL field is the place where you enter an endpoint URL for the composed request.
HTTP Version
The HTTP Version drop-down list renders the following HTTP versions:
Execute Button
The Execute button enables you to effectively execute the composed request. After a successful execution, the Response inspector will be populated with the received response content.
Save Button
The Save button enables you to save the composed request in the [Requests]({%slug saved-requests-tab%}) list. Note that if you are editing an already saved request entry, the changes will overwrite the previous version of that entry. To save the edits as an entirely new entry, use the drop-down option and click Save as (available for already saved requests only).
Headers, Params, Raw, and Body
The middle section allows you to modify your request by adding your custom Headers, Params, and Body, and observing the composed request through the read-only Raw view.
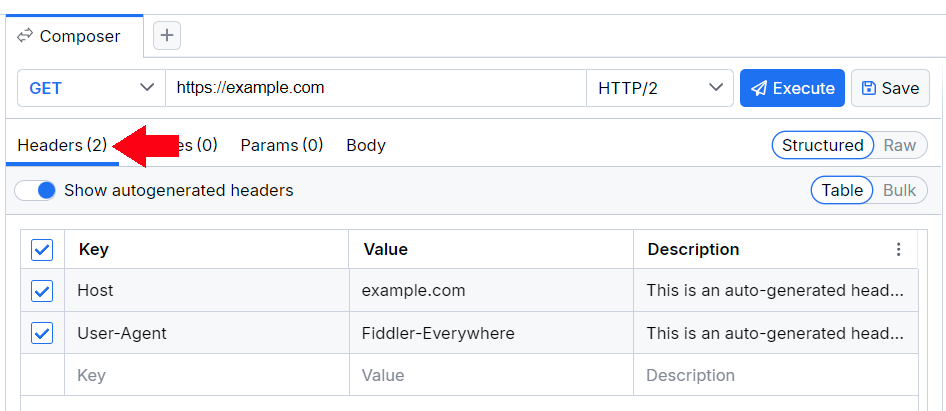
Headers
The Headers section enables you to add or modify your request headers—for example, Content-Type, Authorization, and so on. By default, a key-value UI is activated.
To change it to raw UI through the drop-down in the top-right corner of the section:
-
Add a new header by entering the header key-value pair. Click the tick.
-
The new header is now part of your request headers. The header can now be disabled or enabled by using the tick to the left, or completely deleted by using the Delete icon to the right.
Most of the servers using newer versions of TLS will require you to set Host and User-Agent headers. By default, Fiddler Everywhere automatically generates a User-Agent header set with the Fiddler Everywhere value and a Host header with the respective host value. Note that each HTTP request must include a Host header. The User-Agent header is not mandatory, yet keep in mind that some requests for securing servers might fail without a valid ' User-Agent'. Fiddler Everywhere allows you to uncheck the auto-generated headers, but you must manually add your own to compose valid HTTP requests.
tip The request execution includes only checked headers. Unchecked headers won't be included in the request execution but are saved as part of the composed request (so you can activate them at a later time).
Cookies
The Cookies section enables the creation of key-value pairs usually set through the Cookie header. Respectively, changes made in the Cookie header are also represented in the Cookies table.
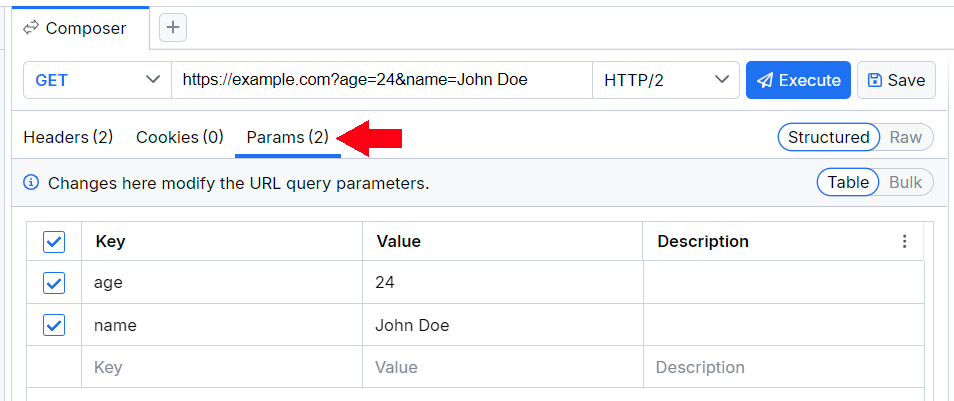
Params
The Params section enables you to add query parameters to your request URL and enables you to add any key-value pair appended through the Params view to the request URL. By default, a key-value UI is activated.
You can change it to raw UI through the drop-down in the top-right corner of the section:
-
Add new query parameters by entering the params key-value pair. Click the tick.
-
The new query parameters are now added to your API endpoint URL. The params can now be disabled or enabled by using the tick to the left, or completely deleted by using the Delete icon to the right.
Body
The Body section enables you to manually specify the data that has to be sent with the request. By default, a key-value UI is activated and you can change it to raw UI through the drop-down in the top-right corner of the section.
The Body delivers the following specific editors:
- Text—suitable for a plain text input (formatted as text/plain)
- JSON—suitable for a JSON-formatted input
- XML—suitable for a XML-formatted input
- HTML—suitable for a HTML-formatted input
- Form-Data—suitable for inputting key-value pairs formatted as multipart/form-data
- x-www-form-urlencoded——suitable for inputting key-value pairs formatted as application/x-www-form-urlencoded
- JavaScript—suitable for JavaScript/TypeScript code. Supports the MIME types as described here
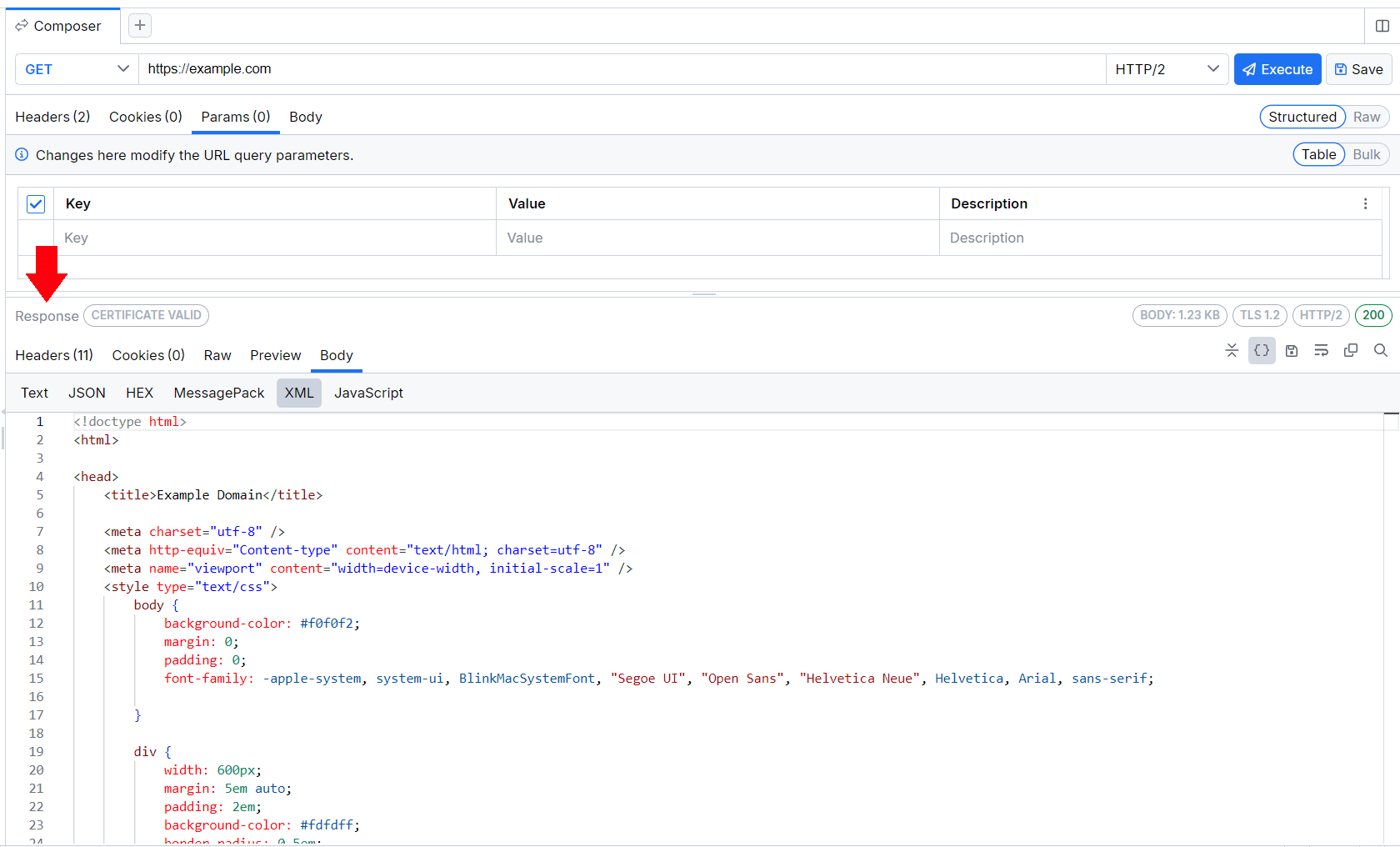
Response Inspector
With the Response Inspector, you can inspect the received response from the executed request. The inspector provides a set of views to visualize different parts of the request in specific formats. For detailed information on each inspector type, refer to the article about [the Inspector types Fiddler Everywhere provides]({%slug inspector-types%}).