21 KiB
 Verify
Verify
Verify is a snapshot tool that simplifies the assertion of complex data models and documents.
Verify is called on the test result during the assertion phase. It serializes that result and stores it in a file that matches the test name. On the next test execution, the result is again serialized and compared to the existing file. The test will fail if the two snapshots do not match: either the change is unexpected, or the reference snapshot needs to be updated to the new result.
See Milestones for release notes.
Requirements
- Supported runtimes: net472, net48, net481, net6, net8, and net9.
- Supported SDK: 8.0.300 and up
Getting started wizard
Get customized instructions for the specific combination of Operating System, IDE, Test Framework, and Build Server.
NuGet packages
- https://nuget.org/packages/Verify.NUnit/
- https://nuget.org/packages/Verify.Xunit/
- https://nuget.org/packages/Verify.XunitV3/
- https://nuget.org/packages/Verify.Fixie/
- https://nuget.org/packages/Verify.Expecto/
- https://nuget.org/packages/Verify.MSTest/
- https://nuget.org/packages/Verify.TUnit/
Snapshot management
Accepting or declining a snapshot file is part of the core workflow of Verify. There are several ways to do this and the approach(s) selected is a personal preference.
- In the Windows Tray via DiffEngineTray
- ReSharper test runner plugin (Source)
- Rider test runner plugin (Source)
- Via the clipboard.
- Manually making the change in the launched diff tool. Either with a copy paste, or some tools have commands to automate this via a shortcut or a button.
- Manually on the file system. By renaming the
.received.file to.verified.. This can be automated via a scripted to bulk accept all (by matching a pattern).received.files. - Using the dotnet tool Verify.Terminal.
Usage
ImplicitUsings
include: implicit-usings
Class being tested
Given a class to be tested:
snippet: ClassBeingTested
NUnit
Support for NUnit
snippet: SampleTestNUnit
xUnit
Support for xUnit
snippet: SampleTestXunit
xUnitV3
Support for xUnitV3
snippet: SampleTestXunitV3
Fixie
Support for Fixie
snippet: SampleTestFixie
include: fixie-convention
Expecto
Support for Expecto
snippet: SampleTestExpecto
Caveats
Due to the nature of the Expecto implementation, the following APIs in Verify are not supported.
settings.UseParameters()settings.UseTextForParameters()
TUnit
Support for TUnit
snippet: SampleTestTUnit
MSTest
Support for MSTest
snippet: SampleTestMSTest
Marking tests as 'Using Verify'
include: mstest-marker
Initial Verification
No existing .verified. file.
graph TD
run(Run test and<br/>create Received file)
failTest(Fail Test<br/>and show Diff)
closeDiff(Close Diff)
run-->failTest
shouldAccept{Accept ?}
failTest-->shouldAccept
accept(Move Received<br/>to Verified)
shouldAccept-- Yes -->accept
discard(Discard<br/>Received)
shouldAccept-- No -->discard
accept-->closeDiff
discard-->closeDiff
When the test is initially run will fail. If a Diff Tool is detected it will display the diff.
To verify the result:
- Execute the command from the Clipboard, or
- Accept with DiffEngineTray tool,
- Accept with ReSharper Addin or Rider Addin
- Use the diff tool to accept the changes, or
- Manually copy the text to the new file
Verified result
This will result in the Sample.Test.verified.txt being created:
snippet: Verify.Xunit.Tests/Snippets/Sample.Test.verified.txt
Subsequent Verification
Existing .verified. file.
graph TD
run(Run test and<br/>create Received file)
closeDiff(Close Diff)
failTest(Fail Test<br/>and show Diff)
run-->isSame
shouldAccept{Accept ?}
failTest-->shouldAccept
accept(Move Received<br/>to Verified)
shouldAccept-- Yes -->accept
discard(Discard<br/>Received)
shouldAccept-- No -->discard
isSame{Compare<br/>Verified +<br/>Received}
passTest(Pass Test and<br/>discard Received)
isSame-- Same --> passTest
isSame-- Different --> failTest
accept-->closeDiff
discard-->closeDiff
If the implementation of ClassBeingTested changes:
snippet: ClassBeingTestedChanged
And the test is re run it will fail.
The Diff Tool will display the diff:
The same approach can be used to verify the results and the change to Sample.Test.verified.txt is committed to source
control along with the change to ClassBeingTested.
Async
Verify() has overloads that accept Task<T>, ValueTask<T>, and IAsyncEnumerable<T>. These are awaited before
verification.
There is also an overload that accepts Func<Task<T>>, which works well with async lambda expressions:
snippet: VerifyFuncOfTaskOfT
VerifyJson
VerifyJson performs the following actions
- Convert to
JToken(if necessary). - Apply ignore member by name for keys.
- PrettyPrint the resulting text.
snippet: VerifyJson
Results in a .txt file:
snippet: JsonTests.VerifyJsonString.verified.txt
Conventions
Source control Includes/Excludes
include: include-exclude
Text file settings
include: text-file-settings
Conventions check
The above conventions can be checked by calling VerifyChecks.Run() in a test
MSTest
snippet: VerifyChecksMSTest
Expecto
snippet: VerifyChecksExpecto
Fixie
snippet: VerifyChecksFixie
Xunit
snippet: VerifyChecksXunit
XunitV3
snippet: VerifyChecksXunitV3
NUnit
snippet: VerifyChecksNUnit
TUnit
snippet: VerifyChecksTUnit
Static settings
Most settings are available at the both global level and at the instance level.
When modifying settings at the both global level it should be done using a Module Initializer:
snippet: StaticSettings.cs
VerifyResult
In some scenarios it can be helpful to get access to the resulting *.verified.* files after a successful run. For
example to do an explicit check for contains or not-contains in the resulting text. To allow this all Verify methods
return a VerifyResult.
snippet: VerifyResult
If using Verifier.Throws, the resulting Exception will also be accessible
snippet: ExceptionResult
CurrentFile
Utility for finding paths based on the current file.
snippet: CurrentFile.cs
Versioning
Verify follows Semantic Versioning. The same applies for extensions to Verify.
Small changes in the resulting snapshot files may be deployed in a minor version. As such nuget updates to Verify.*
should be done as follows:
- Updates all
Verify.*packages in isolation - Re-run all tests.
- If there are changes, ensure they look correct given the release notes. If the changes do not look correct, raise an issue.
- Accept those changes.
Snapshot changes do not trigger a major version change to avoid causing Diamond dependency issues for downstream extensions.
Unit testing inside virtualized environment
Unit tests referencing Verify (including unit tests within this repository as well as any other code
referencing Verify) can be run and debugged on a local virtualized environment supported
by Visual Studio Remote Testing.
Initial configurations have been added for WSL and net 7.0 linux docker via testenvironments.json (for third party
code, the file needs to be copied or recreated next to the .sln solution file for solution to leverage the
functionality).
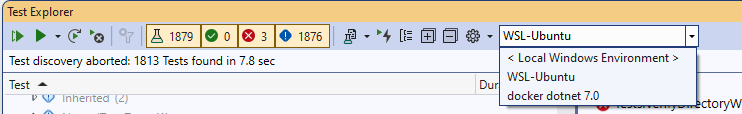
Upon opening the Tests Explorer the advanced environments are available in the GUI:
This readme will not discuss definitive list of details for proper setup of the environments instead refer the following information sources and warn about particular gotchas:
- WSL runs
- Install WSL.
- Install a distribution.
- Install .NET Runtime
- Docker runs
- Install Docker Desktop
- First run of docker scenario might need elevation (Test project does not reference any .NET NuGet adapter error)
- Third party test runners might not support this feature. Use Visual Studio Test Explorer.
Media
Blogs
- Snapshot Testing in .NET with Verify - Khalid Abuhakmeh (12 July 2024)
- Snapshot testing in C# with Verify - Tim Deschryver (21 Feb 2024)
- Snapshot Testing in C# - William Rees (13 Feb 2024)
- I want to do a snapshot test with C# (26 Dec 2023)
- I REGRET Not Telling Dave Farley THIS about Approval Testing - Emily Bache (27 Sep 2023)
- Today's random F# code: Using Verify to prevent breaking changes in stored data - Urs Enzler (31 Mar 2023)
- Compare object values in xUnit C# with Verify - Pierre Belin (18 Nov 2022)
- Unit testing assertions are now easier than ever with Verify Snapshot tool - Rana Krishnrajsinh (5 Nov 2022)
- The easiest way to Unit Test with Verify in C# - Tomasz Juszczak (6 Sep 2022)
- Testing an incremental generator with snapshot testing (14 Dec 2021)
- 5 helpful Nuget package for Unit Testing in .NET (16 Oct 2021)
- Snapshot Testing with Verify: Carl Franklin's Blazor Train (3 Apr 2020)
- Verify: Snapshot Testing for C# (23 Nov 2020)
Podcasts
- Unhandled Exception podcast: Snapshot Testing (26 Nov 2021)
- Snapshot Testing with Verify - Dan Clarke (10 Dec 2021)
Videos
- Introduction to Snapshot testing and using Verify.Xunit - Betatalks (11 Oct 2023)
- The Way to Test Legacy Code in C# - Gui Ferreira (19 Sep 2023)
- Snapshot Testing in .NET with Verify - Dan Clarke (21 Jul 2022)
- Testing C# code reliably by freezing it in time - Nick Chapsas (1 Aug 2022)
- 5 open source .NET projects that deserve more attention (9 Sep 2021)
- OSS Power-Ups: Verify (14 Jul 2021)
- Verify Xunit Intro (26 Apr 2020)
Extensions
- Verify.AngleSharp: Html verification utilities via AngleSharp.
- Verify.AspNetCore: Verification of AspNetCore bits.
- Verify.Aspose: Verification of documents (pdf, docx, xlsx, and pptx) via Aspose.
- Verify.Assertions: Extends Verify to allow an assertion callback. This enables using assertion libraries to interrogate during serialization.
- Verify.AustralianProtectiveMarkings: Verification of AustralianProtectiveMarkings.
- Verify.Avalonia: Verification of Avalonia UIs.
- Verify.Blazor: Verification of Blazor Component Blazor rendering.
- Verify.Bunit: Verification of Blazor Component via bunit.
- Verify.Brighter: Verification of Brighter bits.
- Verify.CommunityToolkit.Mvvm: Verification of CommunityToolkit.Mvvm.
- Verify.Cosmos: Verification of Azure CosmosDB.
- Verify.DiffPlex: Comparison of text via DiffPlex.
- Verify.DocNet: Verification of pdfs via DocNet.
- Verify.EntityFramework: Verification of EntityFramework bits.
- Verify.FakeItEasy: Verification of FakeItEasy bits.
- Verify.Flurl: Verification of Flurl bits.
- Verify.HeadlessBrowsers: Verification of Web UIs using Playwright, Puppeteer Sharp, or Selenium.
- Verify.Http: Verification of Http bits.
- Verify.ICSharpCode.Decompiler: Comparison of assemblies and types via ICSharpCode.Decompiler.
- Verify.ImageHash: Comparison of images via ImageHash.
- Verify.ImageSharp.Compare: Verification and comparison of images via Codeuctivity.ImageSharp.Compare.
- Verify.ImageMagick: Verification and comparison of images via Magick.NET.
- Verify.ImageSharp: Verification of images via ImageSharp.
- Verify.MailMessage: Verification of MailMessage and related types.
- Verify.MassTransit: Support for MassTransit test helpers.
- Verify.MicrosoftLogging: Verify MicrosoftLogging.
- Verify.MongoDB: Verification of MongoDB bits.
- Verify.Moq: Verification of Moq bits.
- Verify.NodaTime: Support for NodaTime.
- Verify.NewtonsoftJson: Support for converting Newtonsoft.Json types (JObject and JArray).
- Verify.NServiceBus: Verify NServiceBus Test Contexts.
- Verify.NSubstitute: Support for NSubstitute types.
- Verify.Nupkg: Verification of NuGet .nupkg files.
- Verify.PdfPig: Verification of pdfs via PdfPig.
- Verify.Phash: Comparison of images via Phash.
- Verify.Quibble: Comparison of objects via Quibble.
- Verify.QuestPDF: Verification of pdf documents via QuestPDF.
- Verify.RavenDb: Verification of RavenDb bits.
- Verify.SendGrid: Verification of SendGrid.
- Verify.Serilog: Verification of Serilog bits.
- Verify.SqlServer: Verification of SqlServer bits.
- Verify.SourceGenerators: Verification of C# Source Generators.
- Verify.SystemJson: Support for converting System.Text.Json types.
- Verify.Terminal: A dotnet tool for managing Verify snapshots.
- Verify.WinForms: Verification of WinForms UIs.
- Verify.Xamarin: Verification of Xamarin UIs.
- Verify.Xaml: Verification of Xaml UIs.
- Spectre.Verify.Extensions: Add an attribute driven file naming convention to Verify.
- Verify.Syncfusion: Verification of documents (pdf, docx, xlsx, and pptx) via Syncfusion File Formats.
- Verify.Wolverine: Verifiable test context for Wolverine.
- Verify.ZeroLog: Verifiable test context for ZeroLog.
More Documentation
include: doc-index
Icon
Helmet designed by Leonidas Ikonomou from The Noun Project.