16 KiB
Semantic Parsing in Context 
The official pytorch implementation of our paper How Far are We from Effective Context Modeling ? An Exploratory Study on Semantic Parsing in Context. This code contains multiple context modeling techniques on modeling context in semantic parsing. It provides readable, fast and strong baselines for the community.
If you find our code useful, please consider citing our paper:
@inproceedings{qian2020how,
title={How Far are We from Effective Context Modeling? An Exploratory Study on Semantic Parsing in Context twitter},
author={Liu, Qian and Chen, Bei and Guo, Jiaqi and Lou, Jian-Guang and Zhou, Bin and Zhang, Dongmei},
booktitle={IJCAI},
year={2020}
}
Content
- Task Introduction
- Model Framework
- Install Requirements
- Prepare Dataset
- Train Model
- Evaluate Model
- Predict on Custom Data
- Demo on Web
- Pretrained Weights
- Fine-grained Analysis
- Frequent Asked Questions
Task

Semantic parsing, which translates a natural language sentence into its corresponding executable logic form (e.g. Structured Query Language, SQL), relieves users from the burden of learning techniques behind the logic form. The majority of previous studies on semantic parsing assume that queries are context-independent and analyze them in isolation. However, in reality, users prefer to interact with systems in a dialogue, where users are allowed to ask context-dependent incomplete questions. That arises the task of Semantic Parsing in Context, which is quite challenging as there are complex contextual phenomena.
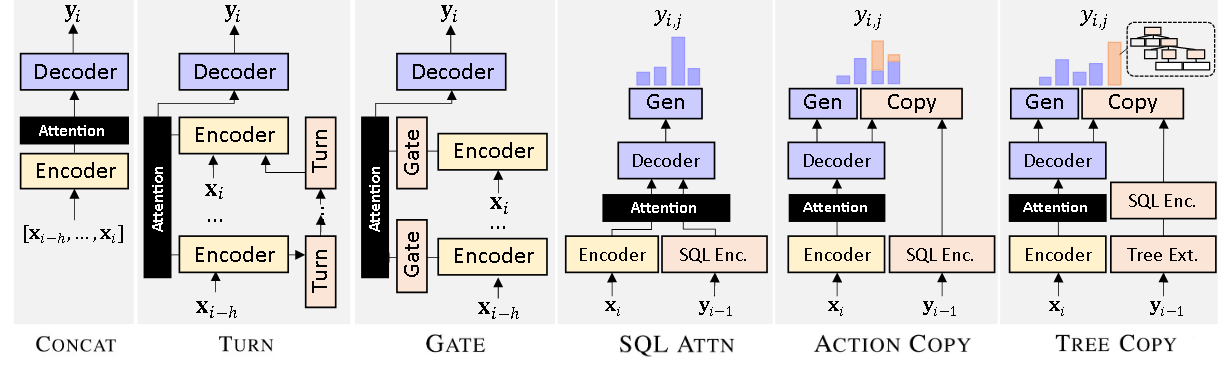
Model

Our backbone is the Sequence to Sequence model with a Grammar-Based Decoder, especially using the IRNet grammar (SemQL).
Requirements
Python Environment
First of all, you should setup a python environment. This code base has been tested under python 3.x, and we officially support python 3.7.
After installing python 3.7, we strongly recommend you to use virtualenv (a tool to create isolated Python environments) to manage the python environment. You could use following commands to create a environment.
python -m pip install virtualenv
virtualenv venv
Activate Virtual Environment
Then you should activate the environment to install the dependencies. You could achieve it via using the command as below. (Please change $ENV_FOLDER to your own virtualenv folder path, e.g. venv)
$ENV_FOLDER\Scripts\activate.bat (Windows)
source $ENV_FOLDER/bin/activate (Linux)
Install Libraries
The most important requirements of our code base are as following:
- pytorch >= 1.2.0 (not tested on other versions, but 1.0.0 may work though)
- allennlp == 0.9.0
Then you should install following packages:
- dill
- ordered_set
- edit_distance
You should install them at first.
SQL-based evaluation
Now our code saves the best model checkpoint based on SQL based comparison, which is the performance indicator on the Spider, SParC and CoSQL benchmarks. Here we adopt the evaluation script which is suited for python3 from EditSQL.
Data
Prepare Dataset
You could download the two datasets SParC and CoSQL. And then rename the dataset top folder as dataset_sparc and dataset_cosql respectively. An example structure for dataset SParC is as following:
|- dataset_sparc
|- database
|- academic
|- activity_1
|- ...
|- train.json
|- dev.json
|- tables.json
|- models
|- predictor
|- ...
Prepare Glove
If you want to train models without BERT, please download Glove Twitter. Unzip and rename the folder into glove.
Train
We use the command allennlp to train our models, and all the hyper-parameters for different settings are stored in configs listed under train_configs and train_configs_bert. The config and model architectures in our paper are as following:
| Config | Model in Paper |
|---|---|
| concat.none.jsonnet | Concat History |
| turn.none.jsonnet | Turn-level Encoder |
| none.attn.jsonnet | SQL Attention |
| none.gate.jsonnet | Gate Mechanism |
| none.token.jsonnet | Action Copy |
| none.tree.jsonnet | Tree Copy |
| concat.attn.jsonnet | Concat + Attention |
| concat.token.jsonnet | Concat + Token Copy |
| concat.tree.jsonnet | Concat + Tree Copy |
| turn.attn.jsonnet | Turn + SQL Attention |
| turn.token.jsonnet | Turn + Action Copy |
| turn.tree.jsonnet | Turn + Tree Copy |
| turn.token.attn.jsonnet | Turn + Action Copy + SQL Attention |
For example, you could run Concat History on SParC using the following script (We also provide windows and linux batch script in the folder batch_files for your convenience. Please run them under the root directory ./.):
- Under linux:
export seed=1
export config_file=train_configs/concat.none.jsonnet
export model_file=checkpoints_sparc/sparc_concat_model
export tables_file=dataset_sparc/tables.json
export database_path=dataset_sparc/database
export dataset_path=dataset_sparc
export train_data_path=dataset_sparc/train.json
export validation_data_path=dataset_sparc/dev.json
export pretrained_file=glove/glove.twitter.27B.100d.txt
allennlp train -s ${model_file} ${config_file} \
--include-package dataset_reader.sparc_reader \
--include-package models.sparc_parser \
-o "{\"model.serialization_dir\":\"${model_file}\",\"random_seed\":\"${seed}\",\"numpy_seed\":\"${seed}\",\"pytorch_seed\":\"${seed}\",\"dataset_reader.tables_file\":\"${tables_file}\",\"dataset_reader.database_path\":\"${database_path}\",\"train_data_path\":\"${train_data_path}\",\"validation_data_path\":\"${validation_data_path}\",\"model.text_embedder.tokens.pretrained_file\":\"${pretrained_file}\",\"model.dataset_path\":\"${dataset_path}\"}"
- Under Windows (
"""is to escape the double quotation mark, equalivant to"):
set seed=1
set config_file=train_configs/concat.none.jsonnet
set model_file=checkpoints_sparc/sparc_concat_model
set tables_file=dataset_sparc/tables.json
set database_path=dataset_sparc/database
set dataset_path=dataset_sparc
set train_data_path=dataset_sparc/train.json
set validation_data_path=dataset_sparc/dev.json
set pretrained_file=glove/glove.twitter.27B.100d.txt
allennlp train -s %model_file% %config_file% ^
--include-package dataset_reader.sparc_reader ^
--include-package models.sparc_parser ^
-o {"""model.serialization_dir""":"""%model_file%""","""random_seed""":"""%seed%""","""numpy_seed""":"""%seed%""","""pytorch_seed""":"""%seed%""","""dataset_reader.tables_file""":"""%tables_file%""","""dataset_reader.database_path""":"""%database_path%""","""train_data_path""":"""%train_data_path%""","""validation_data_path""":"""%validation_data_path%""","""model.text_embedder.tokens.pretrained_file""":"""%pretrained_file%""","""model.dataset_path""":"""%dataset_path%"""}
Evaluate
You could predict and evaluate SQLs using trained model checkpoint file (e.g. checkpoints_sparc/sparc_concat_model/model.tar.gz) using the following command:
- Under Linux
export model_file=checkpoints_sparc/sparc_concat_model
export validation_file=dataset_sparc/dev.json
export validation_out_file=dataset_sparc/dev.jsonl
export prediction_out_file=predict.jsonl
python postprocess.py --valid_file ${validation_file} --valid_out_file ${validation_out_file}
allennlp predict \
--include-package dataset_reader.sparc_reader \
--include-package models.sparc_parser \
--include-package predictor.sparc_predictor \
--predictor sparc \
--dataset-reader-choice validation \
--batch-size 1 \
--cuda-device 0 \
--output-file ${model_file}/${prediction_out_file} \
${model_file}/model.tar.gz ${validation_out_file}
- Under Windows
set model_file=checkpoints_sparc/sparc_concat_model
set validation_file=dataset_sparc/dev.json
set validation_out_file=dataset_sparc/dev.jsonl
set prediction_out_file=predict.jsonl
python postprocess.py --valid_file %validation_file% --valid_out_file %validation_out_file%
allennlp predict ^
--include-package dataset_reader.sparc_reader ^
--include-package models.sparc_parser ^
--include-package predictor.sparc_predictor ^
--predictor sparc ^
--dataset-reader-choice validation ^
--batch-size 1 ^
--cuda-device 0 ^
--output-file %model_file%/%prediction_out_file% ^
%model_file%/model.tar.gz %validation_out_file
Predict On Custom Data
Our code also supports function call to predict SQls on custom data. You could find it in predict.py. Before running it, you should firstly store your own database into paths corresponding to the arguments of PredictManager with the same format as SParC/CoSQL.
Demo
You could also host a demo page using the following command using a well-trained archived model (e.g. checkpoints_sparc/sparc_concat_model/model.tar.gz):
- Under Linux
export model_file=checkpoints_sparc/sparc_concat_model
python -m allennlp.service.server_simple \
--archive-path ${model_file}/model.tar.gz \
--predictor sparc \
--include-package predictor.sparc_predictor \
--include-package dataset_reader.sparc_reader \
--include-package models.sparc_parser \
--title "Contextual Semantic Parsing Demo" \
--field-name question \
--field-name database_id
- Under Windows
set model_file=checkpoints_sparc/sparc_concat_model
python -m allennlp.service.server_simple ^
--archive-path %model_file%/model.tar.gz ^
--predictor sparc ^
--include-package predictor.sparc_predictor ^
--include-package dataset_reader.sparc_reader ^
--include-package models.sparc_parser ^
--title "Contextual Semantic Parsing Demo" ^
--field-name question ^
--field-name database_id
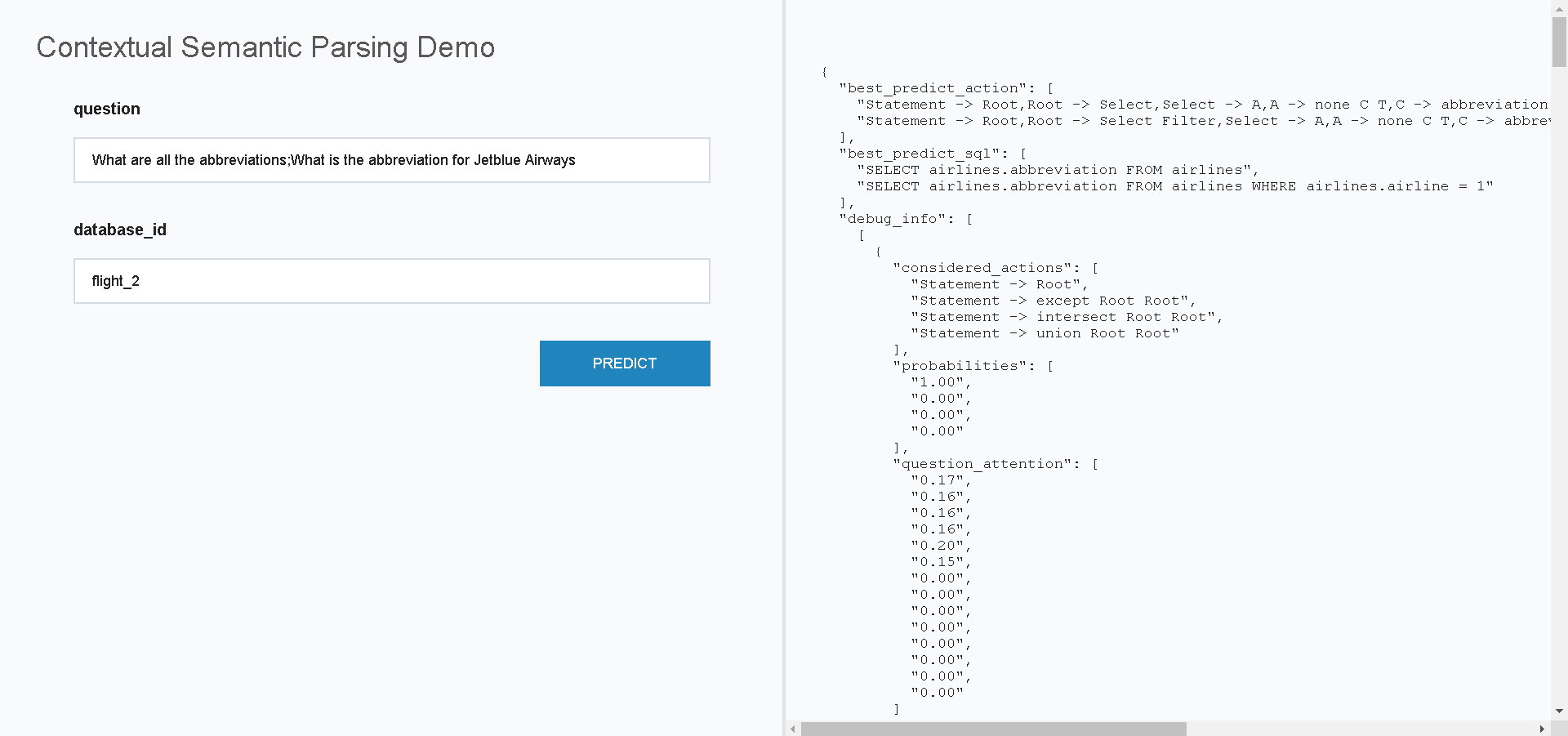
Once running, you could open the demo page in http://localhost:8000. The question field accepts an interaction of questions separated by ;. See the demo page below (only accepts database_id appeared in tables.json):
Experiment
| Dataset | BERT | Config | Best | Avg | Pretrained_Weights |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SParC | No | concat.none.jsonnet | 41.8 | 40.0 | model.tar.gz |
| SParC | No | turn.none.jsonnet | 43.6 | 42.4 | model.tar.gz |
| SParC | No | none.token.jsonnet | 38.9 | 38.4 | model.tar.gz |
| SParC | Yes | concat.none.jsonnet | 52.6 | 51.0 | model.tar.gz |
| SParC | Yes | turn.none.jsonnet | 47.0 | 43.0 | model.tar.gz |
| SParC | Yes | none.token.jsonnet | 46.1 | 45.4 | model.tar.gz |
| CoSQL | No | concat.none.jsonnet | 33.5 | 32.4 | model.tar.gz |
| CoSQL | No | turn.none.jsonnet | 31.9 | 31.3 | model.tar.gz |
| CoSQL | No | none.token.jsonnet | 32.8 | 31.9 | model.tar.gz |
| CoSQL | Yes | concat.none.jsonnet | 41.0 | 40.4 | model.tar.gz |
| CoSQL | Yes | turn.none.jsonnet | 39.2 | 38.9 | model.tar.gz |
| CoSQL | Yes | none.token.jsonnet | 42.1 | 41.6 | model.tar.gz |
Analysis
We also provide the fine-grained analysis results here annotated on the SParC validation set. You could either use it in your research work or debug your model in a fine-grained level.
Acknowledgement
We will thank the following repos which are very helpful to us.
FAQ
1. allennlp.common.checks.ConfigurationError: 'Serialization directory (checkpoints_sparc/sparc_concat_none_model) already exists and is not empty. Specify --recover to recover training from existing output.'
Ans: It means that there is already a checkpoint model named checkpoints_sparc/sparc_concat_none_model. Please add --recover option after the train commnd (if you want to resume the model to continue training) or delete the checkpoint model.
2. FileNotFoundError: [Errno 2] No such file or directory: 'dataset_sparc/train.json'
Ans: Please firstly download datasets and rename them as dataset_sparc and dataset_cosql following the above instructions.
3. The GPU Memory is not enough for running experiments under BERT
Ans: The training of this repo is based on batching interactions rather than single sentences. It means that, even when batch_size is set as 1, one batch contains ~5 NL-SQL pairs (one interaction/dialogue). Therefore, the minimal memory requirement is nearly 17GB in all settings under BERT.
Considering this, we provide a memory friendly config file concat.none.mem.jsonnet. In such a config, data batching is based on natural language sentences rather than interactions. It only needs at least nearly 5GB when using batch_size as 1.
To reduce memory consumed, you could also consider decreasing maximum_history_len hyper-parameter in #57 in sparc_reader.py (the default value is 5). In practise, it also works well under 3 or 4.
4. How to debug my custom model
Ans: We provide debug.py for debugging your custom model. Please change config_file(#9) into your custom one and debug by running debug.py.
5. How to validate the correctness of generated SemQL
Ans: We provide a test script for validating when translating SQL into SemQL. You could copy & modify the following script to achieve your testing goal as below:
def test_example(self):
db_id = "flight_2"
sql_plain = "SELECT * FROM AIRLINES"
sql_clause = """
{
"orderBy": [],
"from": {
"table_units": [
[
"table_unit",
0
]
],
"conds": []
},
"union": null,
"except": null,
"groupBy": [],
"limit": null,
"intersect": null,
"where": [],
"having": [],
"select": [
false,
[
[
0,
[
0,
[
0,
0,
false
],
null
]
]
]
]
}
"""
expected_action_str = "[Statement -> Root, Root -> Select, Select -> A, A -> none C T, C -> *, T -> airlines]"
self.template(sql_plain, sql_clause, db_id, expected_action_str)
db_id,sql_plainandsql_clausecan be found in the dataset, andexpected_action_strcould be set as empty at first until you obtain the correct expected action sequence output.