42 KiB
TypeScript Node Starter
The main purpose of this repository is to show a working Node.js API Server + front-end project and workflow for writing Node code in TypeScript.
It is not a goal to be a comprehensive and definitive guide to making a TypeScript and Node project, but as a working reference maintained by the community. If you are interested in starting a new TypeScript project - check out the bootstrapping tools reference in the TypeScript Website
Table of contents:
Pre-reqs
To build and run this app locally you will need a few things:
Getting started
- Clone the repository
git clone --depth=1 https://github.com/Microsoft/TypeScript-Node-Starter.git <project_name>
- Install dependencies
cd <project_name>
npm install
- Configure your mongoDB server
# create the db directory
sudo mkdir -p /data/db
# give the db correct read/write permissions
sudo chmod 777 /data/db
# starting from macOS 10.15 even the admin cannot create directory at root
# so lets create the db directory under the home directory.
mkdir -p ~/data/db
# user account has automatically read and write permissions for ~/data/db.
- Start your mongoDB server (you'll probably want another command prompt)
mongod
# on macOS 10.15 or above the db directory is under home directory
mongod --dbpath ~/data/db
- Build and run the project
npm run build
npm start
Or, if you're using VS Code, you can use cmd + shift + b to run the default build task (which is mapped to npm run build), and then you can use the command palette (cmd + shift + p) and select Tasks: Run Task > npm: start to run npm start for you.
Note on editors! - TypeScript has great support in every editor, but this project has been pre-configured for use with VS Code. Throughout the README We will try to call out specific places where VS Code really shines or where this project has been set up to take advantage of specific features.
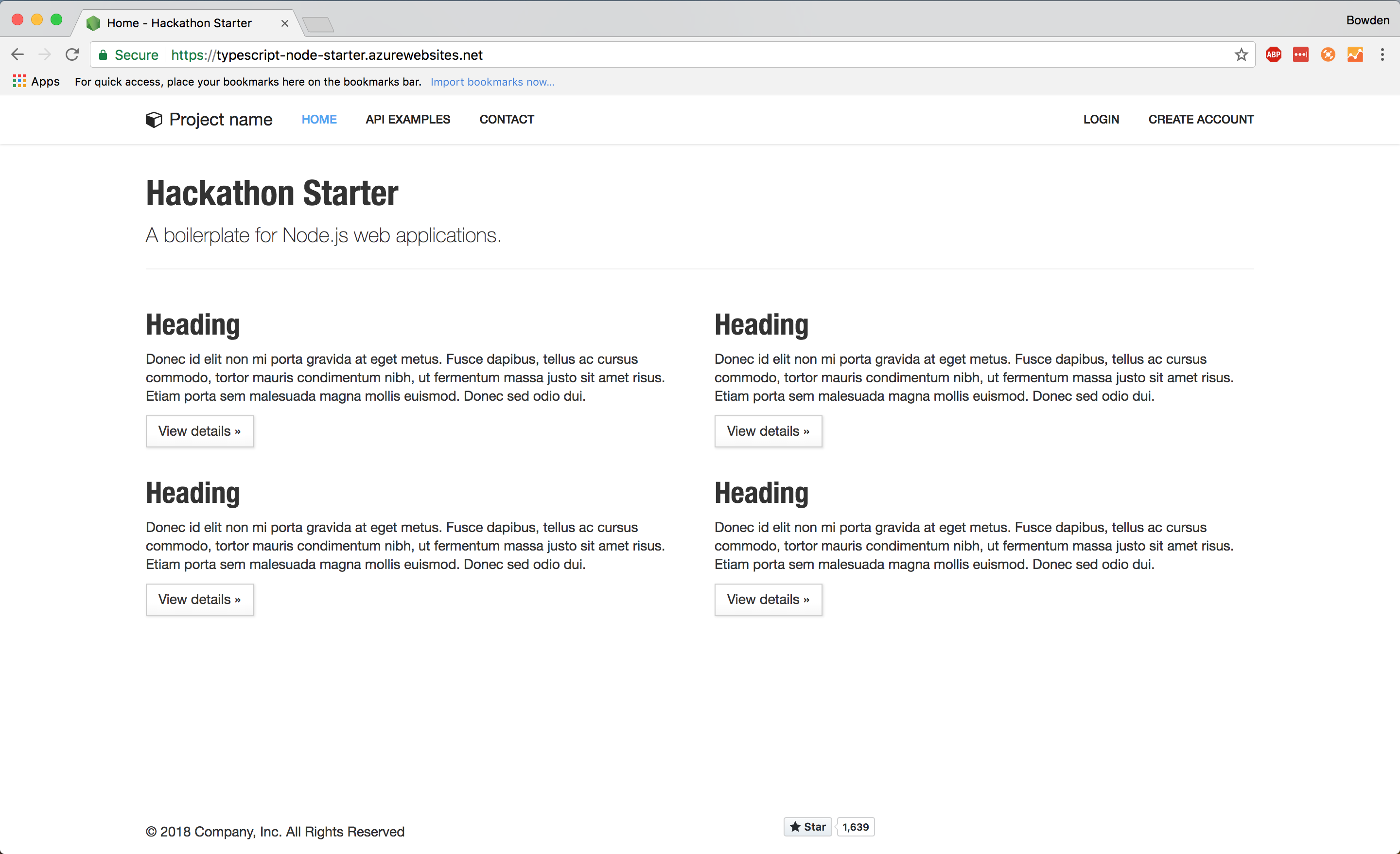
Finally, navigate to http://localhost:3000 and you should see the template being served and rendered locally!
Deploying the app
There are many ways to deploy a Node app, and in general, nothing about the deployment process changes because you're using TypeScript. In this section, I'll walk you through how to deploy this app to Azure App Service using the extensions available in VS Code because I think it is the easiest and fastest way to get started, as well as the most friendly workflow from a developer's perspective.
Prerequisites
- Azure account - If you don't have one, you can sign up for free. The Azure free tier gives you plenty of resources to play around with including up to 10 App Service instances, which is what we will be using.
- VS Code - We'll be using the interface provided by VS Code to quickly deploy our app.
- Azure App Service VS Code extension - In VS Code, search for
Azure App Servicein the extension marketplace (5th button down on the far left menu bar), install the extension, and then reload VS Code. - Create a cloud database - For local development, running MongoDB on localhost is fine, however once we deploy we need a database with high availability. The easiest way to achieve this is by using a managed cloud database. There are many different providers, but the easiest one to get started with is MongoDB Atlas.
- SendGrid Account - If you don't have one, you can sign up for free, we will need it to send emails. There are many different providers that Nodemailer supports (Well-known services), we'll be using SendGrid.
Create a managed MongoDB with Atlas
- Navigate to MongoDB's website, sign up for a free account, and then log in.
- After creating the account, enter the organization name, project name, and select your preferred language (JavaScript).
- Select the Shared Cluster to get a free version with up to 512 MB storage which is great for development purposes.
- On the "Create a Starter Cluster" page you can select cloud provider, region, region, cluster tier, and MongoDB settings, like version and backup frequency (Note: there is no option to create backups in the free tier).
- If you already know to which cloud provider and region you want to deploy later, you should select the same here for best performance. Otherwise select a region close to the location where you plan to deploy the application later.
- Select M0 Sandbox as the Cluster Tier, give your cluster a name, and then click the "Create Cluster" button.
- It will now take a couple of minutes to create the cluster and you will be redirected to the MongoDB Atlas Admin interface.
- Now you must configure access and security before you can use the database.
- To whitelist an IP address, go to the Network Access section and click the "Add IP Address" button. For local development you can select your current IP address.
- Create a user by selecting the Add New Database User in Database Access, adding a username and password (Password Authentication method) and give him read and write access to any database within the cluster. A user account is required to connect to the database, so remember these values because you will need them as part of your connection string.
- Within the Clusters section, click the Connect button in your cluster to connect to the database.
- You could now connect to the cluster using MongoDB Compass, which is a graphical interface (GUI) to interact with the database.
- But we need to select Connect your application to get the connection string, it should look like this:
mongodb+srv://<username>:<password>@your-cluster.12abc.mongodb.net/your-database?retryWrites=true&w=majorityand replace<username>and<password>with the credentials you just created. Back in your project, open your.envfile and updateMONGODB_URIwith your new connection string.NOTE! - If you don't have an
.envfile yet, rename.env.exampleto.envand follow the comments to update the values in that file. - Success!
You can test that it works locally by updating
MONGODB_URI_LOCALto the same connection string you just updated inMONGO_URI. After rebuilding/serving, the app should work, but users that were previously created in local testing will not exist in the new database! Don't forget to return theMONGO_URI_LOCALto your local test database (if you so desire).
You can find more information about how to get started with Atlas here.
SendGrid Account
- Navigate to SendGrid's Website, sign up for a free account, and complete the verification process.
- Open your
.envfile and updateSENDGRID_USERNAMEandSENDGRID_PASSWORDwith your SendGrid username and password respectively.
Deploying to Azure App Service
Deploying from VS Code can be broken into the following steps:
- Authenticate your Azure account in VS Code
- Build your app
- Zip deploy using the Azure App Service extension
Sign in to your Azure account
- Open VS Code
- Expand the Azure App Service menu in the explorer menu
- If you don't see this, you might not have the
Azure App Serviceextension installed. See the pre-reqs section.
- If you don't see this, you might not have the
- Click
Sign in to Azure... - Choose
Copy & Openfrom the resulting dialog- This will open
aka.ms/deviceloginin a browser window. If it doesn't, just navigate there manually.
- This will open
- Paste in the code that is on your clipboard.
- Go back to VS Code, you should now be signed in. You can confirm that everything worked by seeing your Azure subscription listed in the Azure App Service section of the explorer window. Additionally, you should see the email associated with your account listed in the status bar at the bottom of VS Code.
Build the app
Building the app locally is required to generate a zip to deploy because the App Service won't execute build tasks. Build the app however you normally would:
ctrl + shift + b- kicks off default build in VS Code- execute
npm run buildfrom a terminal window
Zip deploy from VS Code
- Make sure your app is built, whatever is currently in your
distandnode_modulesfolders will be the app that is deployed. - Click the blue up arrow (Deploy to Web App) on the Azure App Service section of the explorer window.
- Choose the entire project directory.
If you haven't changed the name, this will be
TypeScript-Node-Starter. - Choose the subscription you want this app to be billed to (don't worry, it will be free).
- Choose
Create New Web App - Enter a globally unique name - This will be part of the URL that azure generates, so it has to be unique, but if you're planning on adding a custom domain later, it's not that important. I usually just add random numbers to the end of the app name, ie. typescript-node-starter-15121214.
- Choose a resource group - If you don't know what this is, just create a new one. If you have lots of cloud resources that should be logically grouped together (think an app service, and a database that supports that app) then you would want to put them in the same resource group. This can always be updated later though. If you create a new resource group, you'll also be prompted to pick a location for that group. Pick something geographically close to where your users are.
- Choose
Create new App Service Plan- An app service plan mainly is what determines the size and cost of the hardware your app will run on, but it also manages some other settings which we can ignore for now. - Choose
B1 - Basic- This one is free. If you know what you're doing, feel free to select a stronger pricing tier. - Choose your target node runtime version - We are deploying to Linux machines, and in addition we can choose the exact node runtime we want. If you don't know what you want, choose whatever the current LTS build is.
- Grab a cup of coffee - You'll see everything you just selected getting created in the output window. All of this is powered by the Azure CLI and can be easily replicated if you decide you want to customize this process. This deployment is not the fastest option (but it is the easiest!). We are literally bundling everything in your project (including the massive node_modules folder) and uploading it to our Azure app service. Times will vary, but as a baseline, my deployment took roughly 6 minutes.
- Add
NODE_ENVenvironment variable - In the App Service section of the explorer window, expand the newly created service, right click on Application Settings, select Add New Settings..., and addNODE_ENVas the key andproductionas the value. This setting determines which database to point to. If you haven't created a cloud database yet, see [the setup instructions](#Create a managed MongoDB with MongoLab). - Profit!
Troubleshooting failed deployments
Deployment can fail for various reasons, if you get stuck with a page that says Service Unavailable or some other error, open an issue and I'll try to help you resolve the problems.
TypeScript + Node
In the next few sections I will call out everything that changes when adding TypeScript to an Express project. Note that all of this has already been set up for this project, but feel free to use this as a reference for converting other Node.js projects to TypeScript.
Getting TypeScript
TypeScript itself is simple to add to any project with npm.
npm install -D typescript
If you're using VS Code then you're good to go!
VS Code will detect and use the TypeScript version you have installed in your node_modules folder.
For other editors, make sure you have the corresponding TypeScript plugin.
Project Structure
The most obvious difference in a TypeScript + Node project is the folder structure.
In a TypeScript project, it's best to have separate source and distributable files.
TypeScript (.ts) files live in your src folder and after compilation are output as JavaScript (.js) in the dist folder.
The test and views folders remain top level as expected.
The full folder structure of this app is explained below:
Note! Make sure you have already built the app using
npm run build
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| .vscode | Contains VS Code specific settings |
| .github | Contains GitHub settings and configurations, including the GitHub Actions workflows |
| dist | Contains the distributable (or output) from your TypeScript build. This is the code you ship |
| node_modules | Contains all your npm dependencies |
| src | Contains your source code that will be compiled to the dist dir |
| src/config | Passport authentication strategies and login middleware. Add other complex config code here |
| src/controllers | Controllers define functions that respond to various http requests |
| src/models | Models define Mongoose schemas that will be used in storing and retrieving data from MongoDB |
| src/public | Static assets that will be used client side |
| src/types | Holds .d.ts files not found on DefinitelyTyped. Covered more in this section |
| src/server.ts | Entry point to your express app |
| test | Contains your tests. Separate from source because there is a different build process. |
| views | Views define how your app renders on the client. In this case we're using pug |
| .env.example | API keys, tokens, passwords, database URI. Clone this, but don't check it in to public repos. |
| .travis.yml | Used to configure Travis CI build |
| .copyStaticAssets.ts | Build script that copies images, fonts, and JS libs to the dist folder |
| jest.config.js | Used to configure Jest running tests written in TypeScript |
| package.json | File that contains npm dependencies as well as build scripts |
| tsconfig.json | Config settings for compiling server code written in TypeScript |
| tsconfig.tests.json | Config settings for compiling tests written in TypeScript |
| .eslintrc | Config settings for ESLint code style checking |
| .eslintignore | Config settings for paths to exclude from linting |
Building the project
It is rare for JavaScript projects not to have some kind of build pipeline these days, however Node projects typically have the least amount of build configuration. Because of this I've tried to keep the build as simple as possible. If you're concerned about compile time, the main watch task takes ~2s to refresh.
Configuring TypeScript compilation
TypeScript uses the file tsconfig.json to adjust project compile options.
Let's dissect this project's tsconfig.json, starting with the compilerOptions which details how your project is compiled.
"compilerOptions": {
"module": "commonjs",
"esModuleInterop": true,
"target": "es6",
"noImplicitAny": true,
"moduleResolution": "node",
"sourceMap": true,
"outDir": "dist",
"baseUrl": ".",
"paths": {
"*": [
"node_modules/*",
"src/types/*"
]
}
},
compilerOptions |
Description |
|---|---|
"module": "commonjs" |
The output module type (in your .js files). Node uses commonjs, so that is what we use |
"esModuleInterop": true, |
Allows usage of an alternate module import syntax: import foo from 'foo'; |
"target": "es6" |
The output language level. Node supports ES6, so we can target that here |
"noImplicitAny": true |
Enables a stricter setting which throws errors when something has a default any value |
"moduleResolution": "node" |
TypeScript attempts to mimic Node's module resolution strategy. Read more here |
"sourceMap": true |
We want source maps to be output along side our JavaScript. See the debugging section |
"outDir": "dist" |
Location to output .js files after compilation |
"baseUrl": "." |
Part of configuring module resolution. See path mapping section |
paths: {...} |
Part of configuring module resolution. See path mapping section |
The rest of the file define the TypeScript project context.
The project context is basically a set of options that determine which files are compiled when the compiler is invoked with a specific tsconfig.json.
In this case, we use the following to define our project context:
"include": [
"src/**/*"
]
include takes an array of glob patterns of files to include in the compilation.
This project is fairly simple and all of our .ts files are under the src folder.
For more complex setups, you can include an exclude array of glob patterns that removes specific files from the set defined with include.
There is also a files option which takes an array of individual file names which overrides both include and exclude.
Running the build
All the different build steps are orchestrated via npm scripts.
Npm scripts basically allow us to call (and chain) terminal commands via npm.
This is nice because most JavaScript tools have easy to use command line utilities allowing us to not need grunt or gulp to manage our builds.
If you open package.json, you will see a scripts section with all the different scripts you can call.
To call a script, simply run npm run <script-name> from the command line.
You'll notice that npm scripts can call each other which makes it easy to compose complex builds out of simple individual build scripts.
Below is a list of all the scripts this template has available:
| Npm Script | Description |
|---|---|
build-sass |
Compiles all .scss files to .css files |
build-ts |
Compiles all source .ts files to .js files in the dist folder |
build |
Full build. Runs ALL build tasks (build-sass, build-ts, lint, copy-static-assets) |
copy-static-assets |
Calls script that copies JS libs, fonts, and images to dist directory |
debug |
Performs a full build and then serves the app in watch mode |
lint |
Runs ESLint on project files |
serve-debug |
Runs the app with the --inspect flag |
serve |
Runs node on dist/server.js which is the apps entry point |
start |
Does the same as 'npm run serve'. Can be invoked with npm start |
test |
Runs tests using Jest test runner |
watch-debug |
The same as watch but includes the --inspect flag so you can attach a debugger |
watch-node |
Runs node with nodemon so the process restarts if it crashes. Used in the main watch task |
watch-sass |
Same as build-sass but continuously watches .scss files and re-compiles when needed |
watch-test |
Runs tests in watch mode |
watch-ts |
Same as build-ts but continuously watches .ts files and re-compiles when needed |
watch |
Runs all watch tasks (TypeScript, Sass, Node). Use this if you're not touching static assets. |
Type Definition (.d.ts) Files
TypeScript uses .d.ts files to provide types for JavaScript libraries that were not written in TypeScript.
This is great because once you have a .d.ts file, TypeScript can type check that library and provide you better help in your editor.
The TypeScript community actively shares all the most up-to-date .d.ts files for popular libraries on a GitHub repository called DefinitelyTyped.
Making sure that your .d.ts files are setup correctly is super important because once they're in place, you get an incredible amount of high quality type checking (and thus bug catching, IntelliSense, and other editor tools) for free.
Note! Because we're using
"noImplicitAny": true, we are required to have a.d.tsfile for every library we use. While you could setnoImplicitAnytofalseto silence errors about missing.d.tsfiles, it is a best practice to have a.d.tsfile for every library. (Even if the.d.tsfile is basically empty!)
Installing .d.ts files from DefinitelyTyped
For the most part, you'll find .d.ts files for the libraries you are using on DefinitelyTyped.
These .d.ts files can be easily installed into your project by using the npm scope @types.
For example, if we want the .d.ts file for jQuery, we can do so with npm install --save-dev @types/jquery.
Note! Be sure to add
--save-dev(or-D) to yournpm install..d.tsfiles are project dependencies, but only used at compile time and thus should be dev dependencies.
In this template, all the .d.ts files have already been added to devDependencies in package.json, so you will get everything you need after running your first npm install.
Once .d.ts files have been installed using npm, you should see them in your node_modules/@types folder.
The compiler will always look in this folder for .d.ts files when resolving JavaScript libraries.
What if a library isn't on DefinitelyTyped?
If you try to install a .d.ts file from @types and it isn't found, or you check DefinitelyTyped and cannot find a specific library, you will want to create your own .d.ts file.
In the src folder of this project, you'll find the types folder which holds the .d.ts files that aren't on DefinitelyTyped (or weren't as of the time of this writing).
Setting up TypeScript to look for .d.ts files in another folder
The compiler knows to look in node_modules/@types by default, but to help the compiler find our own .d.ts files we have to configure path mapping in our tsconfig.json.
Path mapping can get pretty confusing, but the basic idea is that the TypeScript compiler will look in specific places, in a specific order when resolving modules, and we have the ability to tell the compiler exactly how to do it.
In the tsconfig.json for this project you'll see the following:
"baseUrl": ".",
"paths": {
"*": [
"node_modules/*",
"src/types/*"
]
}
This tells the TypeScript compiler that in addition to looking in node_modules/@types for every import (*) also look in our own .d.ts file location <baseUrl> + src/types/*.
So when we write something like:
import * as flash from "express-flash";
First the compiler will look for a d.ts file in node_modules/@types and then when it doesn't find one look in src/types and find our file express-flash.d.ts.
Using dts-gen
Unless you are familiar with .d.ts files, I strongly recommend trying to use the tool dts-gen first.
The README does a great job explaining how to use the tool, and for most cases, you'll get an excellent scaffold of a .d.ts file to start with.
In this project, bcrypt-nodejs.d.ts, fbgraph.d.ts, and lusca.d.ts were all generated using dts-gen.
Writing a .d.ts file
If generating a .d.ts using dts-gen isn't working, you should tell me about it first, but then you can create your own .d.ts file.
If you just want to silence the compiler for the time being, create a file called <some-library>.d.ts in your types folder and then add this line of code:
declare module "<some-library>";
If you want to invest some time into making a great .d.ts file that will give you great type checking and IntelliSense, the TypeScript website has great docs on authoring .d.ts files.
Contributing to DefinitelyTyped
The reason it's so easy to get great .d.ts files for most libraries is that developers like you contribute their work back to DefinitelyTyped.
Contributing .d.ts files is a great way to get into the open source community if it's something you've never tried before, and as soon as your changes are accepted, every other developer in the world has access to your work.
If you're interested in giving it a shot, check out the guidance on DefinitelyTyped. If you're not interested, you should tell me why so we can help make it easier in the future!
Summary of .d.ts management
In general if you stick to the following steps you should have minimal .d.ts issues;
- After installing any npm package as a dependency or dev dependency, immediately try to install the
.d.tsfile via@types. - If the library has a
.d.tsfile on DefinitelyTyped, the installation will succeed, and you are done. If the install fails because the package doesn't exist, continue to step 3. - Make sure you project is configured for supplying your own
d.tsfiles - Try to generate a
.d.tsfile with dts-gen. If it succeeds, you are done. If not, continue to step 5. - Create a file called
<some-library>.d.tsin yourtypesfolder. - Add the following code:
declare module "<some-library>";
- At this point everything should compile with no errors, and you can either improve the types in the
.d.tsfile by following this guide on authoring.d.tsfiles or continue with no types. - If you are still having issues, let me know by emailing me or pinging me on twitter, I will help you.
Debugging
Debugging TypeScript is exactly like debugging JavaScript with one caveat, you need source maps.
Source maps
Source maps allow you to drop break points in your TypeScript source code and have that break point be hit by the JavaScript that is being executed at runtime.
Note! - Source maps aren't specific to TypeScript. Anytime JavaScript is transformed (transpiled, compiled, optimized, minified, etc) you need source maps so that the code that is executed at runtime can be mapped back to the source that generated it.
The best part of source maps is when configured correctly, you don't even know they exist! So let's take a look at how we do that in this project.
Configuring source maps
First you need to make sure your tsconfig.json has source map generation enabled:
"compilerOptions" {
"sourceMap": true
}
With this option enabled, next to every .js file that the TypeScript compiler outputs there will be a .map.js file as well.
This .map.js file provides the information necessary to map back to the source .ts file while debugging.
Note! - It is also possible to generate "inline" source maps using
"inlineSourceMap": true. This is more common when writing client side code because some bundlers need inline source maps to preserve the mapping through the bundle. Because we are writing Node.js code, we don't have to worry about this.
Using the debugger in VS Code
Debugging is one of the places where VS Code really shines over other editors. Node.js debugging in VS Code is easy to set up and even easier to use. This project comes pre-configured with everything you need to get started.
When you hit F5 in VS Code, it looks for a top level .vscode folder with a launch.json file.
You can debug in the following ways:
- Launch Program - transpile typescript to javascript via npm build, then launch the app with the debugger attached on startup
- Attach by Process ID - run the project in debug mode. This is mostly identical to the "Node.js: Attach by Process ID" template with one minor change.
We added
"protocol": "inspector"which tells VS Code that we're using the latest version of Node which uses a new debug protocol. - Jest Current File - have a Jest test file open and active in VSCode, then debug this specific file by setting break point. All tests are not run.
- Jest all - run all tests, set a break point.
In this file, you can tell VS Code exactly what you want to do:
[
{
"name": "Launch Program",
"type": "node",
"program": "${workspaceFolder}/dist/server.js",
"request": "launch",
"preLaunchTask": "npm: build"
},
{
"type": "node",
"request": "attach",
"name": "Attach by Process ID",
"processId": "${command:PickProcess}",
"protocol": "inspector"
},
{
"type": "node",
"request": "launch",
"name": "Jest Current File",
"program": "${workspaceFolder}/node_modules/.bin/jest",
"args": [
"${fileBasenameNoExtension}",
"--detectOpenHandles"
],
"console": "integratedTerminal",
"internalConsoleOptions": "neverOpen",
"disableOptimisticBPs": true,
"windows": {
"program": "${workspaceFolder}/node_modules/jest/bin/jest",
}
},
{
"type": "node",
"request": "launch",
"name": "Jest all",
"runtimeExecutable": "npm",
"runtimeArgs": [
"run-script",
"test"
],
"port": 9229,
"skipFiles": [
"<node_internals>/**"
]
},
]
With this file in place, you can hit F5 to attach a debugger.
You will probably have multiple node processes running, so you need to find the one that shows node dist/server.js.
Now just set your breakpoints and go!
Testing
For this project, I chose Jest as our test framework. While Mocha is probably more common, Mocha seems to be looking for a new maintainer and setting up TypeScript testing in Jest is wicked simple.
Install the components
To add TypeScript + Jest support, first install a few npm packages:
npm install -D jest ts-jest
jest is the testing framework itself, and ts-jest is just a simple function to make running TypeScript tests a little easier.
Configure Jest
Jest's configuration lives in jest.config.js, so let's open it up and add the following code:
module.exports = {
globals: {
'ts-jest': {
tsconfigFile: 'tsconfig.json'
}
},
moduleFileExtensions: [
'ts',
'js'
],
transform: {
'^.+\\.(ts|tsx)$': './node_modules/ts-jest/preprocessor.js'
},
testMatch: [
'**/test/**/*.test.(ts|js)'
],
testEnvironment: 'node'
};
Basically we are telling Jest that we want it to consume all files that match the pattern "**/test/**/*.test.(ts|js)" (all .test.ts/.test.js files in the test folder), but we want to preprocess the .ts files first.
This preprocess step is very flexible, but in our case, we just want to compile our TypeScript to JavaScript using our tsconfig.json.
This all happens in memory when you run the tests, so there are no output .js test files for you to manage.
Running tests
Simply run npm run test.
Note this will also generate a coverage report.
Writing tests
Writing tests for web apps has entire books dedicated to it and best practices are strongly influenced by personal style, so I'm deliberately avoiding discussing how or when to write tests in this guide. However, if prescriptive guidance on testing is something that you're interested in, let me know, I'll do some homework and get back to you.
ESLint
ESLint is a code linter which mainly helps catch quickly minor code quality and style issues.
ESLint rules
Like most linters, ESLint has a wide set of configurable rules as well as support for custom rule sets.
All rules are configured through .eslintrc configuration file.
In this project, we are using a fairly basic set of rules with no additional custom rules.
Running ESLint
Like the rest of our build steps, we use npm scripts to invoke ESLint. To run ESLint you can call the main build script or just the ESLint task.
npm run build // runs full build including ESLint
npm run lint // runs only ESLint
Notice that ESLint is not a part of the main watch task.
If you are interested in seeing ESLint feedback as soon as possible, I strongly recommend the VS Code ESLint extension.
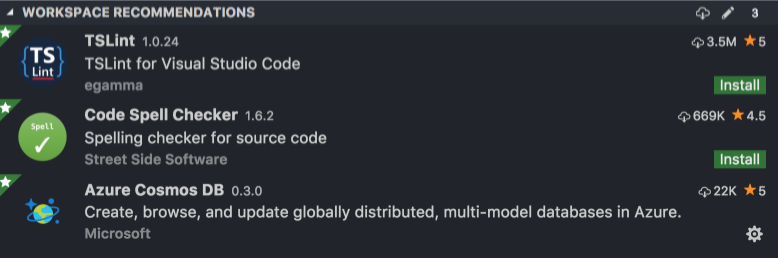
VSCode Extensions
To enhance your development experience while working in VSCode we also provide you a list of the suggested extensions for working with this project:
Dependencies
Dependencies are managed through package.json.
In that file you'll find two sections:
dependencies
| Package | Description |
|---|---|
| async | Utility library that provides asynchronous control flow. |
| bcrypt-nodejs | Library for hashing and salting user passwords. |
| bluebird | Promise library |
| body-parser | Express 4 middleware. |
| compression | Express 4 middleware. |
| connect-mongo | MongoDB session store for Express. |
| dotenv | Loads environment variables from .env file. |
| errorhandler | Express 4 middleware. |
| express | Node.js web framework. |
| express-flash | Provides flash messages for Express. |
| express-session | Express 4 middleware. |
| express-validator | Easy form validation for Express. |
| fbgraph | Facebook Graph API library. |
| lodash | General utility library. |
| lusca | CSRF middleware. |
| mongoose | MongoDB ODM. |
| nodemailer | Node.js library for sending emails. |
| passport | Simple and elegant authentication library for node.js |
| passport-facebook | Sign-in with Facebook plugin. |
| passport-local | Sign-in with Username and Password plugin. |
| pug (jade) | Template engine for Express. |
| request | Simplified HTTP request library. |
| request-promise | Promisified HTTP request library. Let's us use async/await |
| winston | Logging library |
devDependencies
| Package | Description |
|---|---|
| @types | Dependencies in this folder are .d.ts files used to provide types |
| chai | Testing utility library that makes it easier to write tests |
| concurrently | Utility that manages multiple concurrent tasks. Used with npm scripts |
| jest | Testing library for JavaScript. |
| sass | Allows to compile .scss files to .css |
| nodemon | Utility that automatically restarts node process when it crashes |
| supertest | HTTP assertion library. |
| ts-jest | A preprocessor with sourcemap support to help use TypeScript with Jest. |
| ts-node | Enables directly running TS files. Used to run copy-static-assets.ts |
| eslint | Linter for JavaScript and TypeScript files |
| typescript | JavaScript compiler/type checker that boosts JavaScript productivity |
To install or update these dependencies you can use npm install or npm update.
Hackathon Starter Project
A majority of this quick start's content was inspired or adapted from Sahat's excellent Hackathon Starter project.
License
Copyright (c) Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved. Licensed under the MIT License.